Usage
I. Reference
The package documentation preprint is currently available in ArXiv under:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.06976
Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06976
The TensorConvolution+ algorithm was published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid and can be read and referenced using:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2024.3453667
Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10663439
II. Acknowledgements
The authors are part of the IEPG group and AI Energy lab of TU Delft. This research is part of the research program ‘MegaMind - Measuring, Gathering, Mining and Integrating Data for Self-management in the Edge of the Electricity System’, (partly) financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO) through the Perspectief program under number P19-25.




III. Package
The proposed package includes the functionalities to perform flexibility area estimation.
To install the package using pip, run:
(.venv) $ pip install tensorconvolutionplus
To install the package through a file, place the tensorconvolutionplus-0.1.0.tar.gz file in an accessible path and run:
(.venv) $ pip install path/to/package/tensorconvolutionplus-0.1.0.tar.gz
Main functionalities include:
- TensorConvolution+, estimating FAs using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network (names) for MV Oberrhein0, MV Oberrhein1, Cigre MV. If another network is in similar format as these pandapower networks, it can also be an input instead.
Resolutions for the discretization of the flexibility resources.
Network voltage and loading constraints.
Voltage and loading sensitivity thresholds.
Including/Excluding FSPs only offering full output reductions, or limited setpoints ( including these FSPs currently uses the numpy library and not pytorch).
Flexibility service providers.
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
- Shape of flexibility resources. Currently FSP limits are:
the output cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP (resulting in a semi-oval shape),
the output P cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP, the output abs(Q) cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP (resulting in rectangular shape).
additional shapes can be adopted by modifying the sample generation function (not impacting the TensorConvolution+ aggregation).
- TensorConvolution+, while storing estimated tensors and other useful information to adapt flexibility areas for different operating conditions. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network (names) for MV Oberrhein0, MV Oberrhein1, Cigre MV. If another network is in similar format as these pandapower networks, it can also be an input instead.
Resolutions for the discretization of the flexibility resources.
Network voltage and loading constraints.
Voltage and loading sensitivity thresholds.
Flexibility service providers.
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
- Shape of flexibility resources. Currently FSP limits are:
the output cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP (resulting in a semi-oval shape),
the output P cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP, the output abs(Q) cannot exceed the maximum apparent power of the FSP (resulting in rectangular shape).
additional shapes can be adopted by modifying the sample generation function (not impacting the TensorConvolution+ aggregation).
- TensorConvolution+, while loading previously estimated tensors and other useful information to adapt flexibility areas from prior different operating conditions. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network (names) for MV Oberrhein0, MV Oberrhein1, Cigre MV. If another network is in similar format as these pandapower networks, it can also be an input instead. The network must be the same as the stored one.
Resolutions for the discretization of the flexibility resources. Must be the same as the stored simulation.
Network voltage and loading constraints.
Flexibility service providers. Must be the same as the stored simulation.
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
Shape of flexibility resources. Must be the same as the stored simulation.
- Monte Carlo power flow based flexibility area estimation. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network (names) for MV Oberrhein0, MV Oberrhein1, Cigre MV. If another network is in similar format as these pandapower networks, it can also be an input instead.
Network voltage and loading constraints.
Number of samples.
- Distribution used for samples, including:
‘Hard’: Exploring the limit from each resource flexibility.
‘Uniform’: Applying uniform distribution.
‘Kumaraswamy’: Applying the Kumaraswamy distribution.
Flexibility service providers.
Including/Excluding FSPs only offering full output reductions, or limited setpoints (including these FSPs currently uses the numpy library and not pytorch).
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
- Exhaustive power flow based flexibility area estimation. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network (names) for MV Oberrhein0, MV Oberrhein1, Cigre MV. If another network is in similar format as these pandapower networks, it can also be an input instead.
Network voltage and loading constraints.
Resolutions for the discretization of the flexibility resources.
Flexibility service providers.
Including/Excluding FSPs only offering full output reductions, or limited setpoints (including these FSPs currently uses the numpy library and not pytorch).
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
- Optimal power flow based flexibility area estimation. In the current version, the estimations can vary in:
Pandapower network. Cigre MV in radial structure converges whereas alternative networks might fail to converge.
Network voltage and loading constraints. Transformer loading is excluded due to convergence issues.
Flexibility service providers.
Network structure and initial operating conditions.
IV. Examples
All main functionalities require first importing the FA_Estimator script from the package. Therefore, all the following examples start with the Python line:
from TensorConvolutionPlus import FA_Estimator as TCP
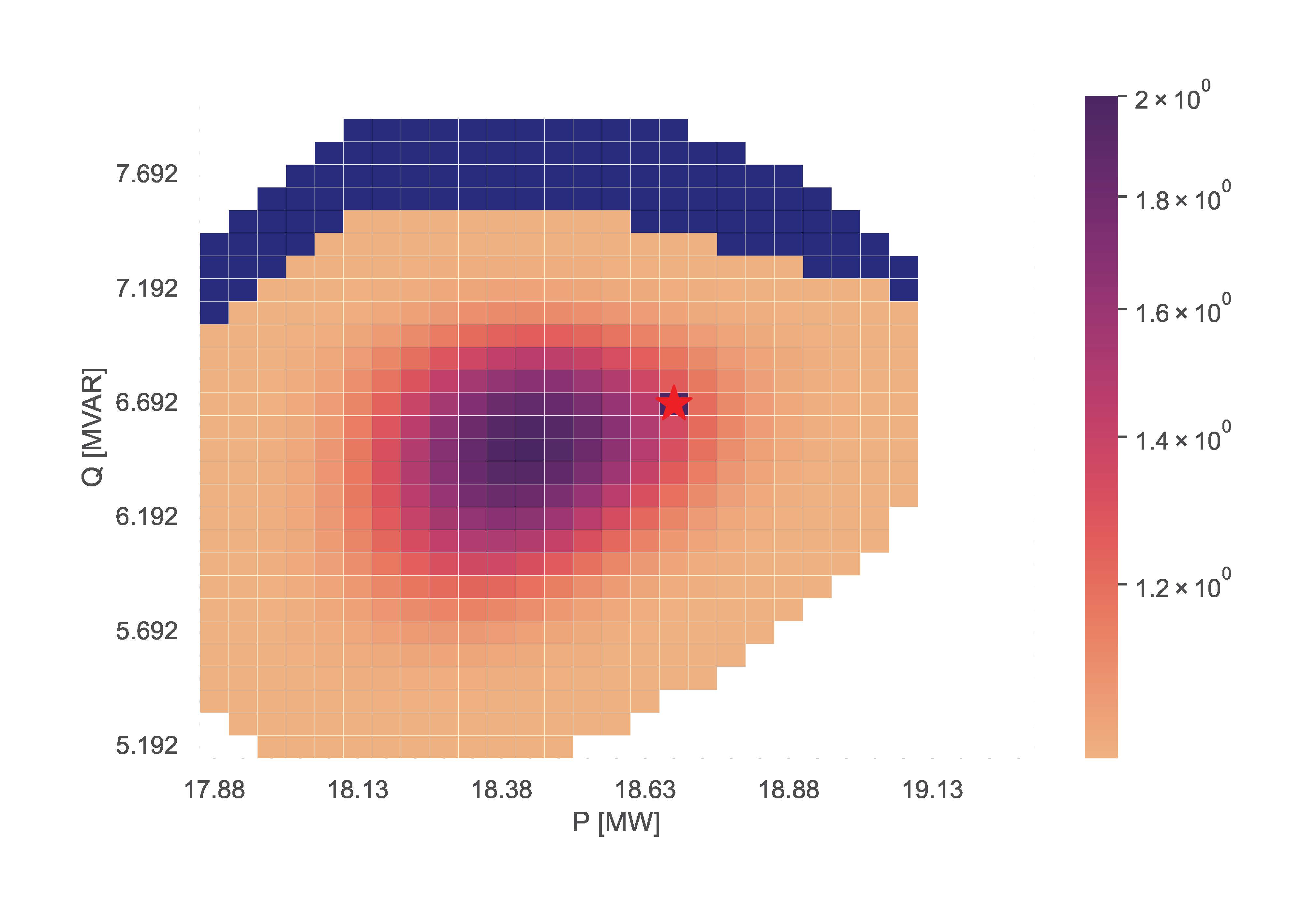
IV.A) Monte Carlo Power Flow
This section includes examples using the Monte Carlo PF estimation functionality. These examples used the Python script code:
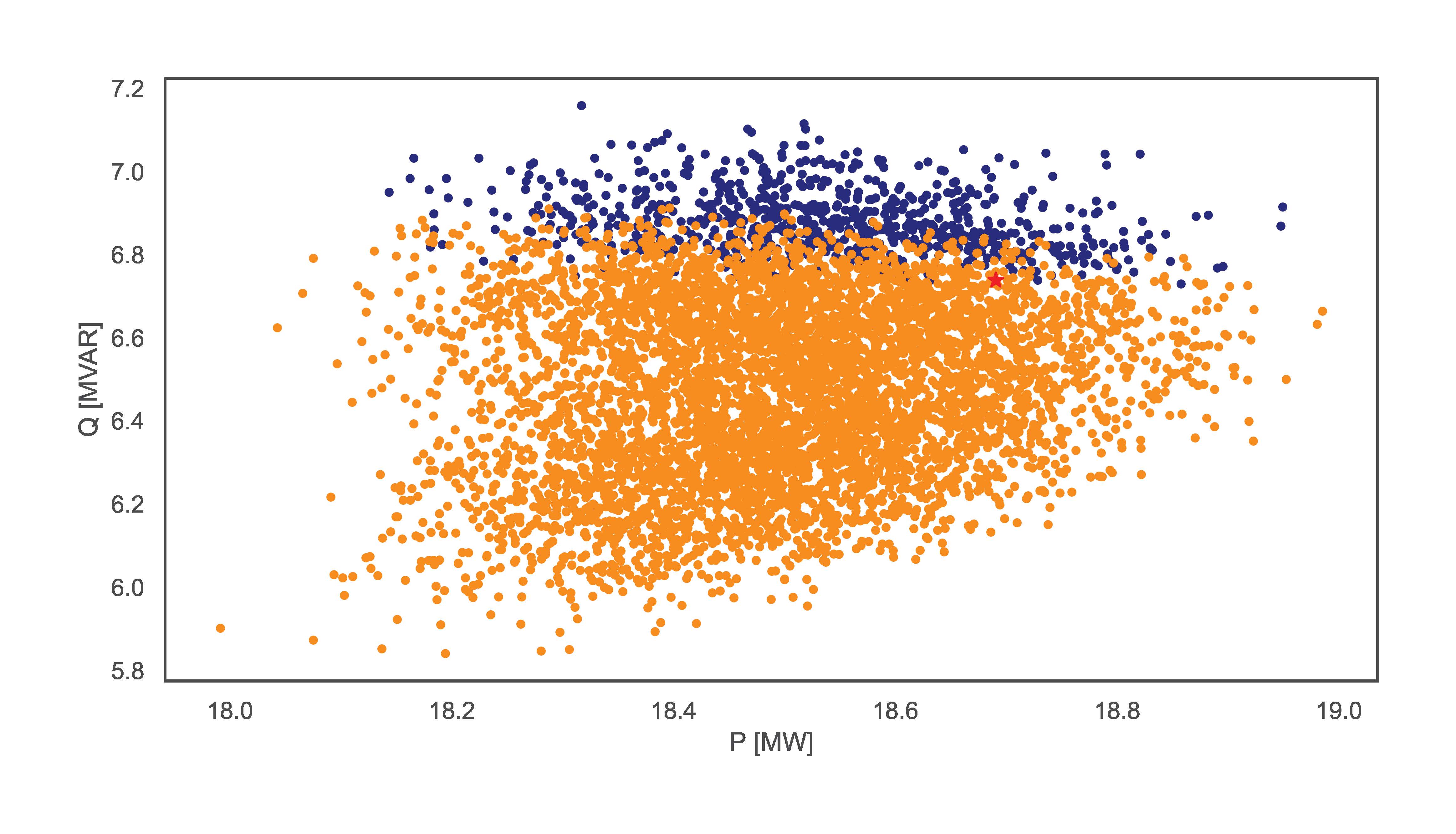
TCP.monte_carlo_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', no_samples=6000, fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3], distribution='Uniform')
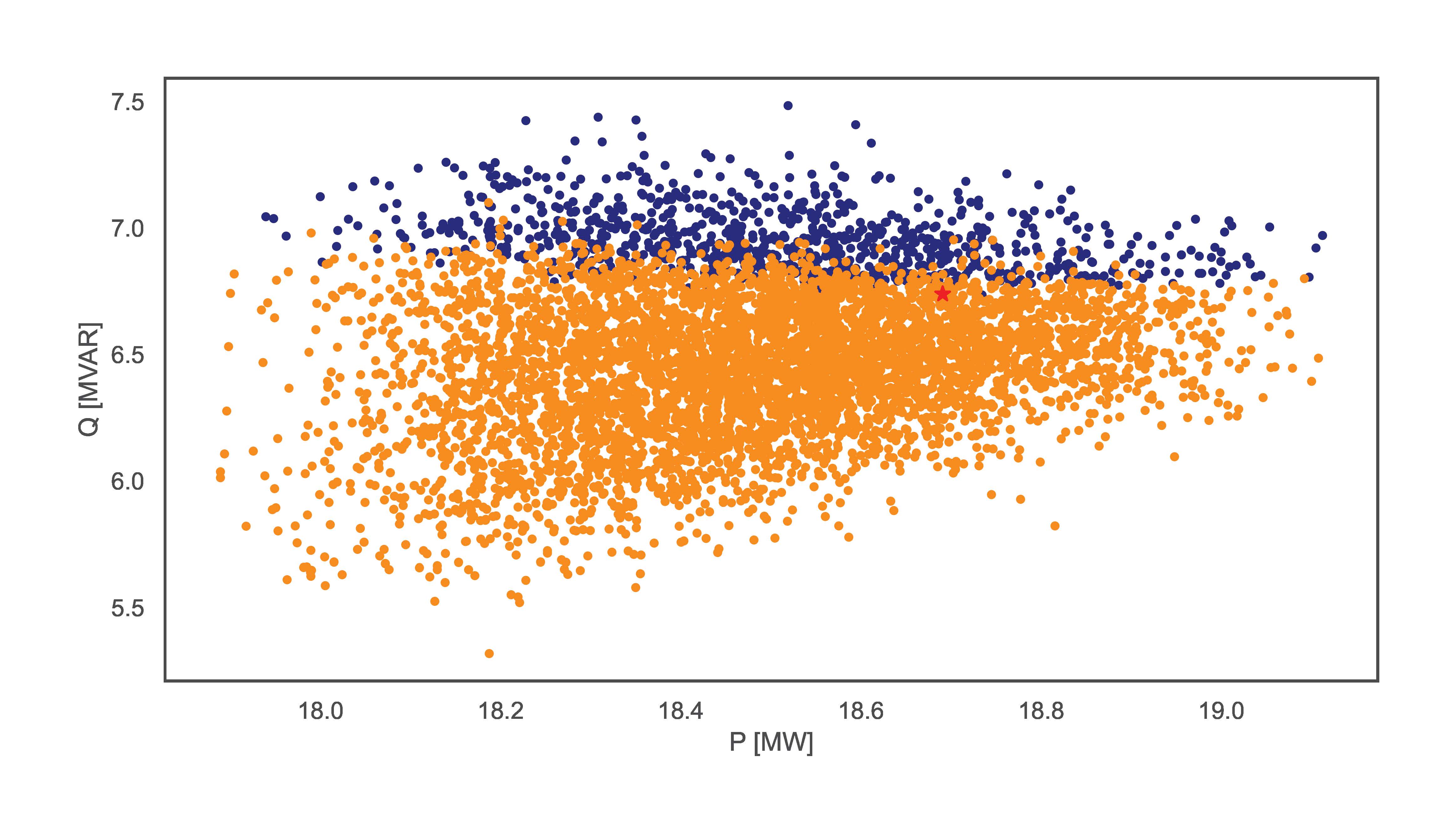
TCP.monte_carlo_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', no_samples=6000, fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3], distribution='Kumaraswamy')
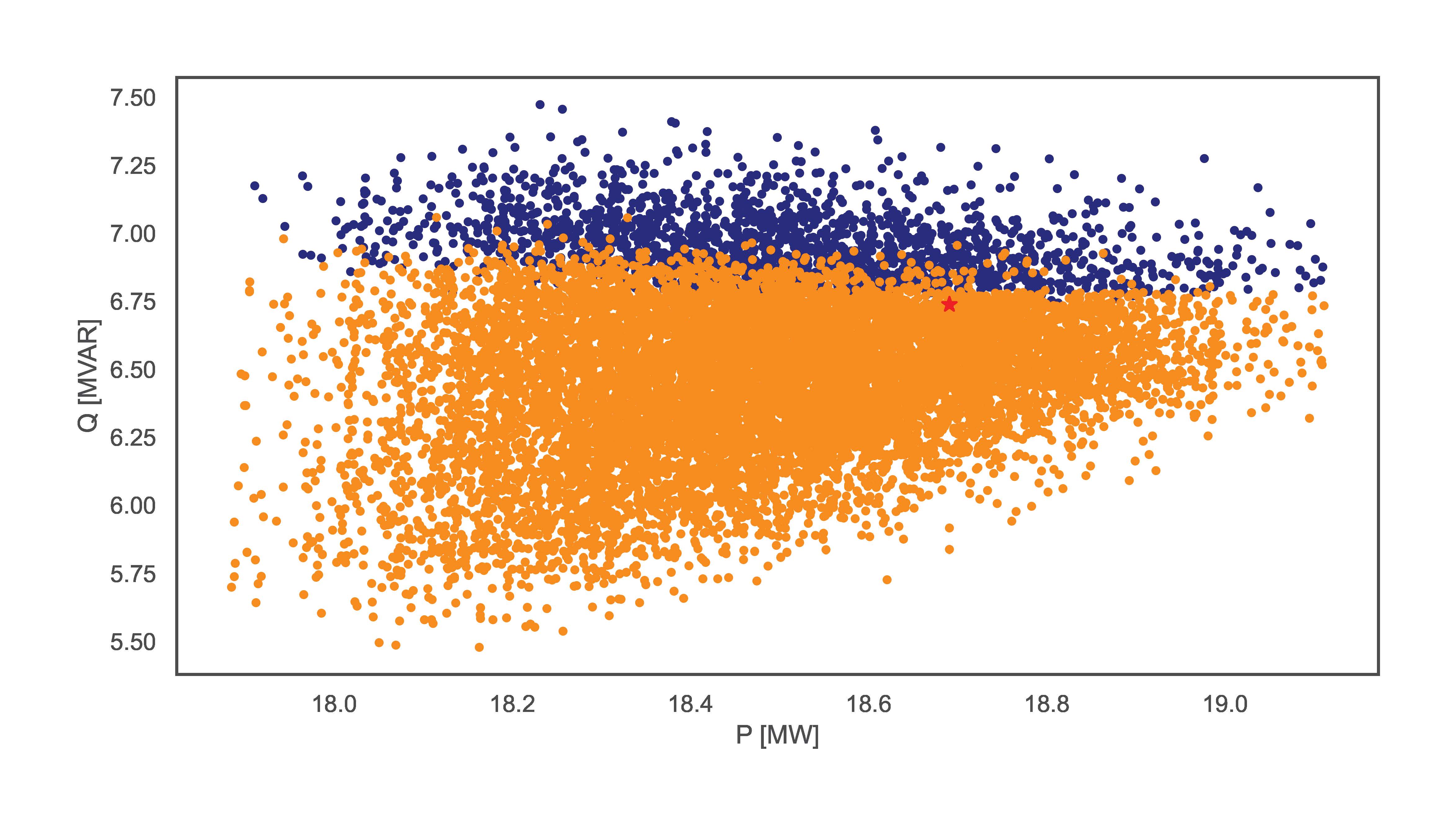
TCP.monte_carlo_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', no_samples=6000, fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3])
TCP.monte_carlo_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', no_samples=12000, fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3])
The examples vary in sampling distribution and number of samples. The figures bellow illustrate the resulting FA for each line respectively. The lines without distribution input automatically obtain the ‘Hard’ distribution.

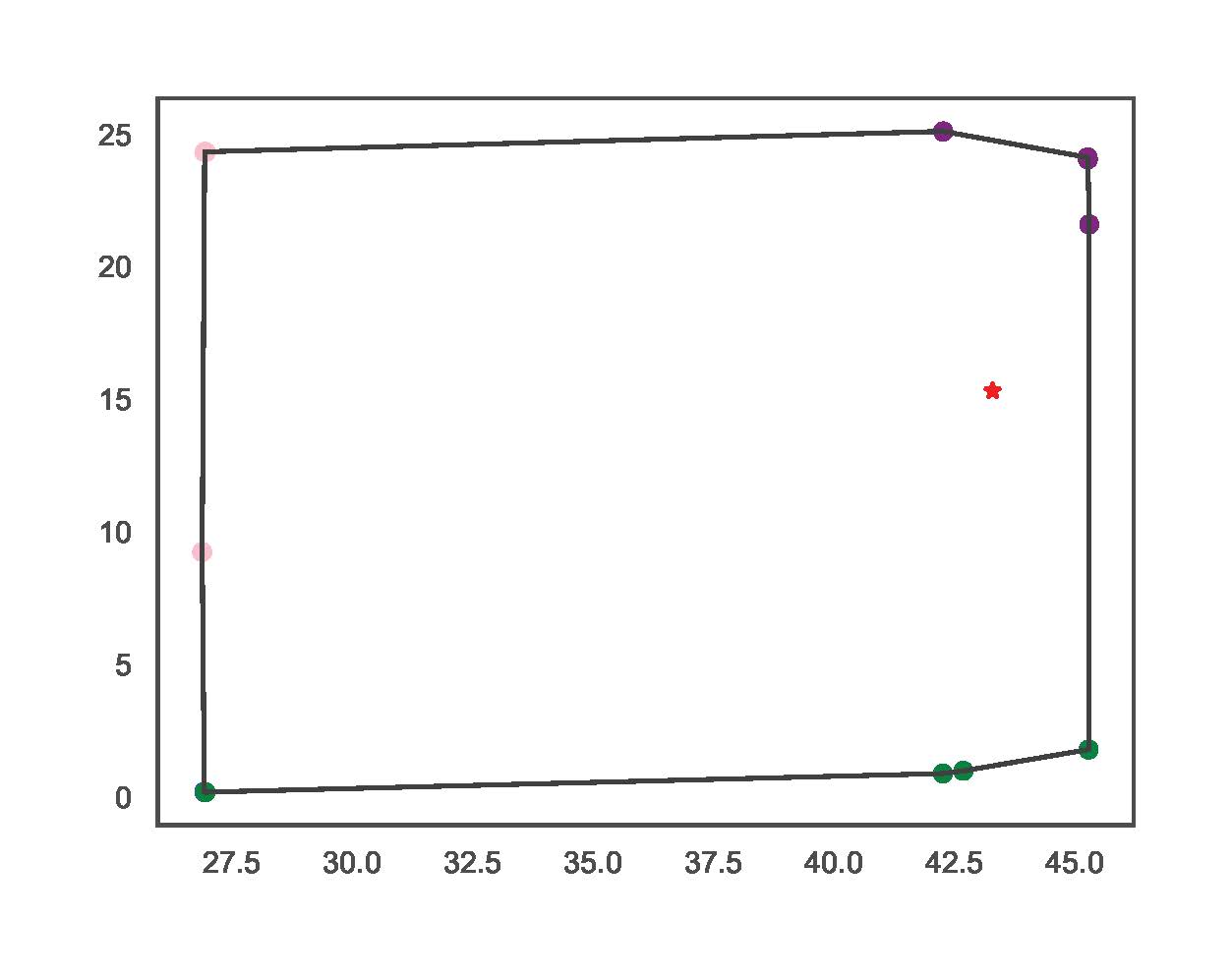
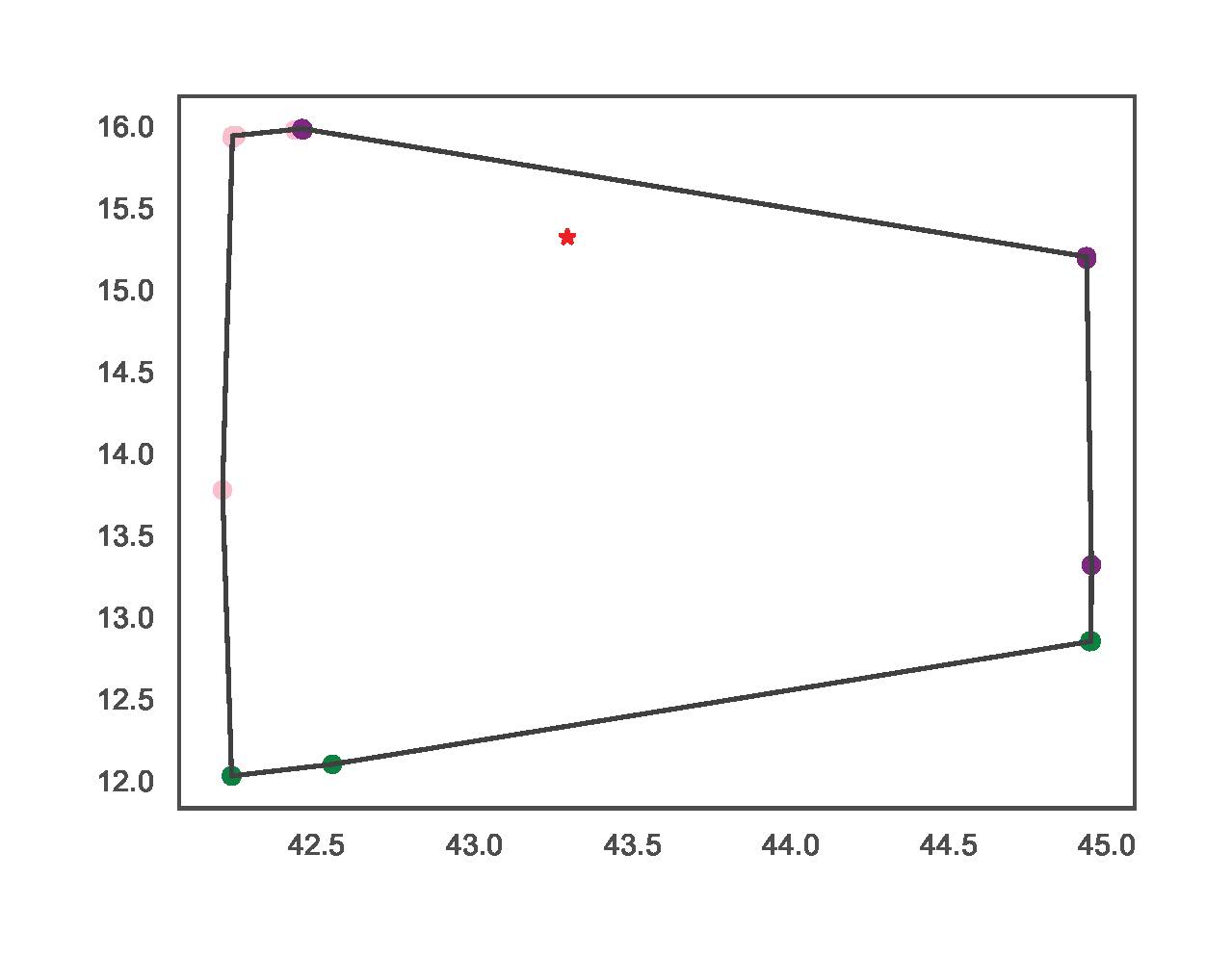
IV.B) Exhaustive Power Flow
This section includes examples using the exhaustive power flow-based functionality. The script for the examples is:
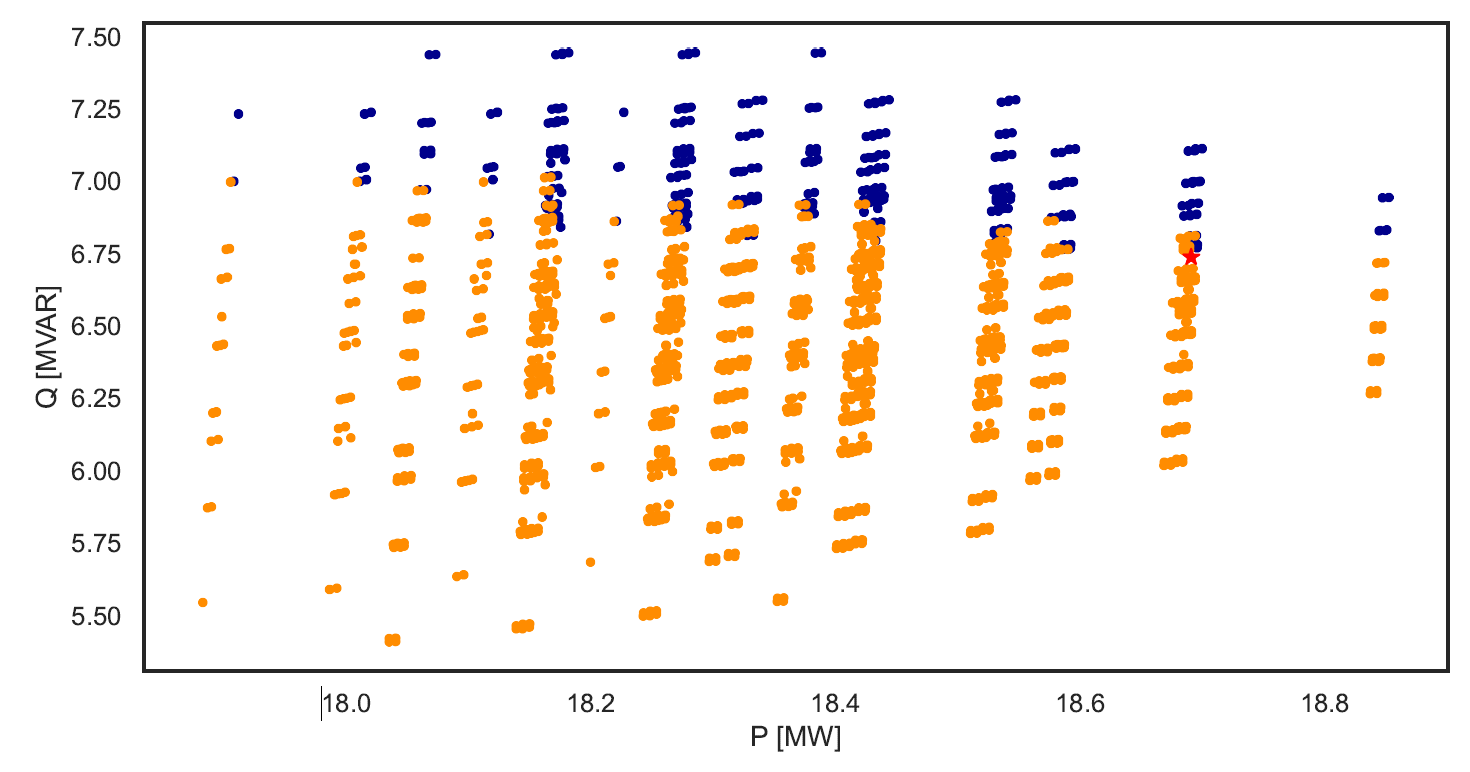
TCP.exhaustive_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', dp=0.15, dq=0.3, fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3])
TCP.exhaustive_pf(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', dp=0.01, dq=0.02, fsp_load_indices=[5], fsp_dg_indices=[5])
The examples vary in resolution and number of FSPs. The figures bellow illustrate the resulting FA for each line respectively.
IV.C) Optimal Power Flow
This section illustrates examples using the OPF estimation functionality. These examples used the Python script code:
TCP.opf(net_name='CIGRE MV', opf_step=0.1, fsp_load_indices=[3, 5, 8], fsp_dg_indices=[8])
TCP.opf(net_name='CIGRE MV', opf_step=0.1, fsp_load_indices=[1, 4, 9], fsp_dg_indices=[8])
The examples vary in FSPs. The figures bellow illustrate the resulting FA for each line respectively.
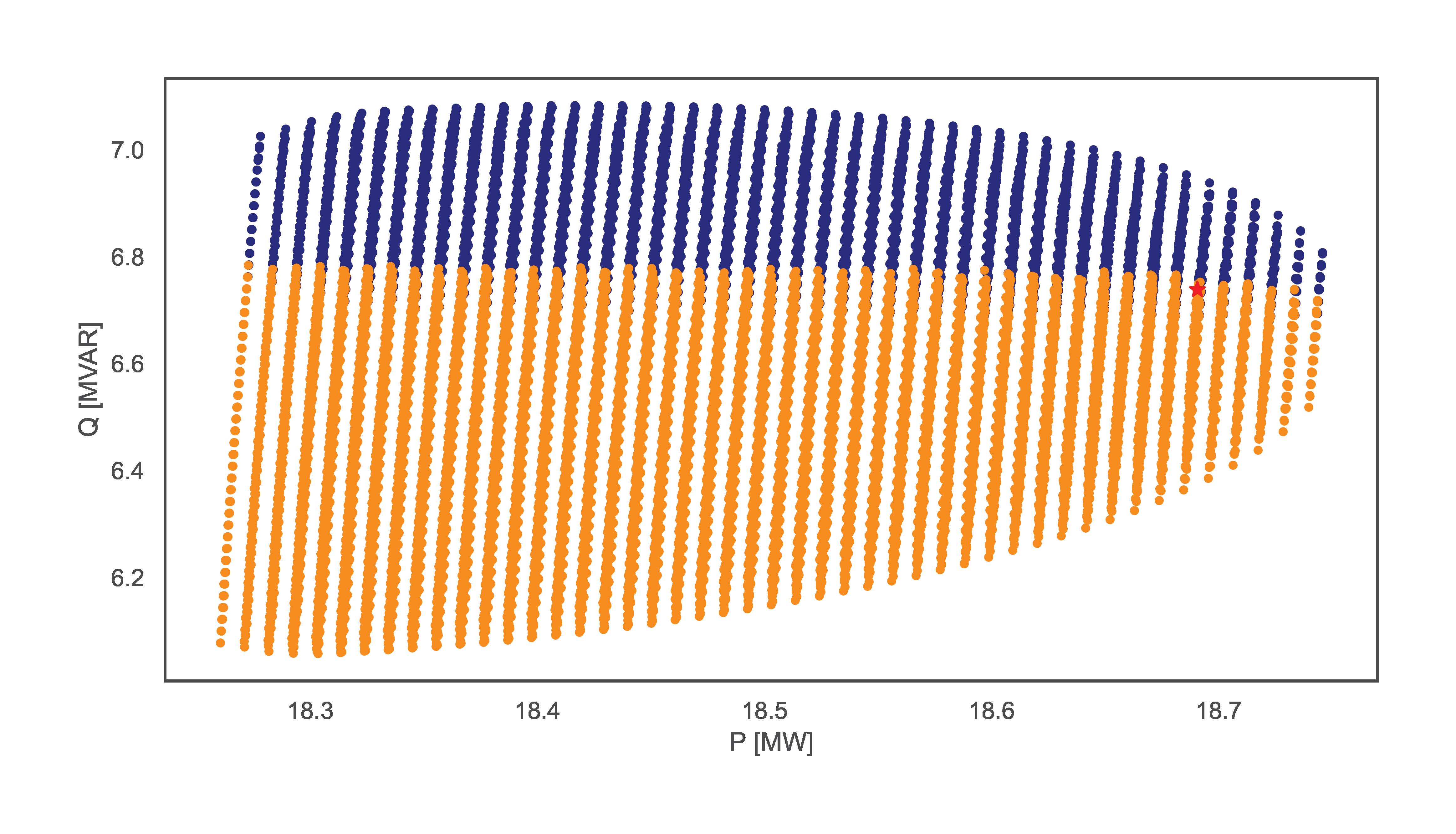
IV.D) TensorConvolution+
This section illustrates examples using the TensorConvolution+ FA estimation functionality. The first examples, showcasing the different shapes of flexibility from FSPs use the lines:
TCP.tc_plus(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], dp=0.05, dq=0.1, fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3])
TCP.tc_plus(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', fsp_load_indices=[1, 2], dp=0.05, dq=0.1, fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2], flex_shape='PQmax')
The examples vary in number of FSPs and shapes of flexibility offers. The example without the flex_shape input automatically obtains the value ‘Smax’. The figures bellow illustrate the resulting FA for each line respectively.

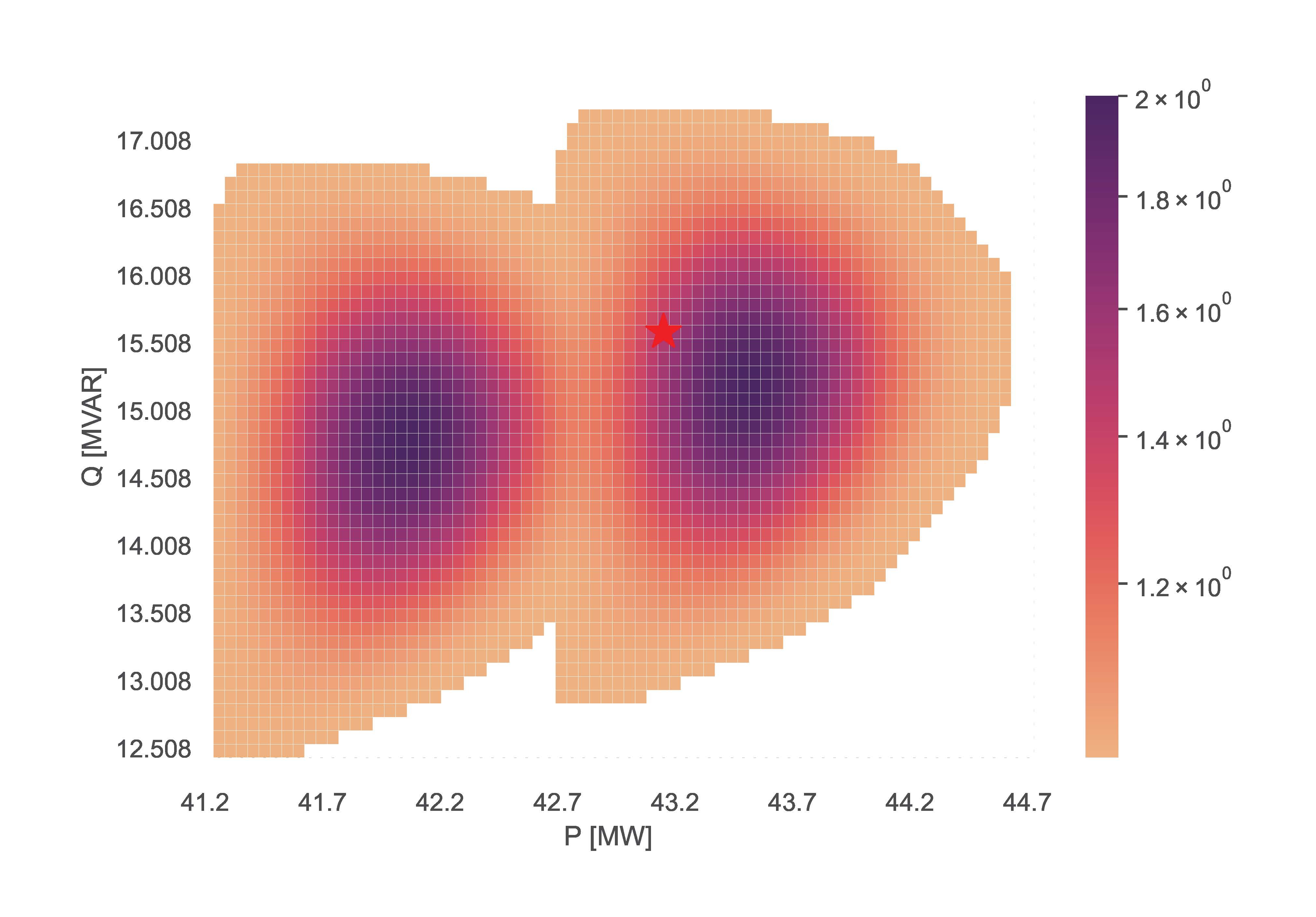
TensorConvolution+ can also simulate FAs with FSPs offering discrete setpoints of flexibility. For such scenarios, the input non_linear_fsps specifies which of the FSPs are non linear. The example line is:
TCP.tc_plus(net_name='CIGRE MV', fsp_load_indices=[3, 4, 5], dp=0.05, dq=0.1, fsp_dg_indices=[8], non_linear_fsps=[8])
The resulting figure is:
IV.E) TensorConvolution+ Merge
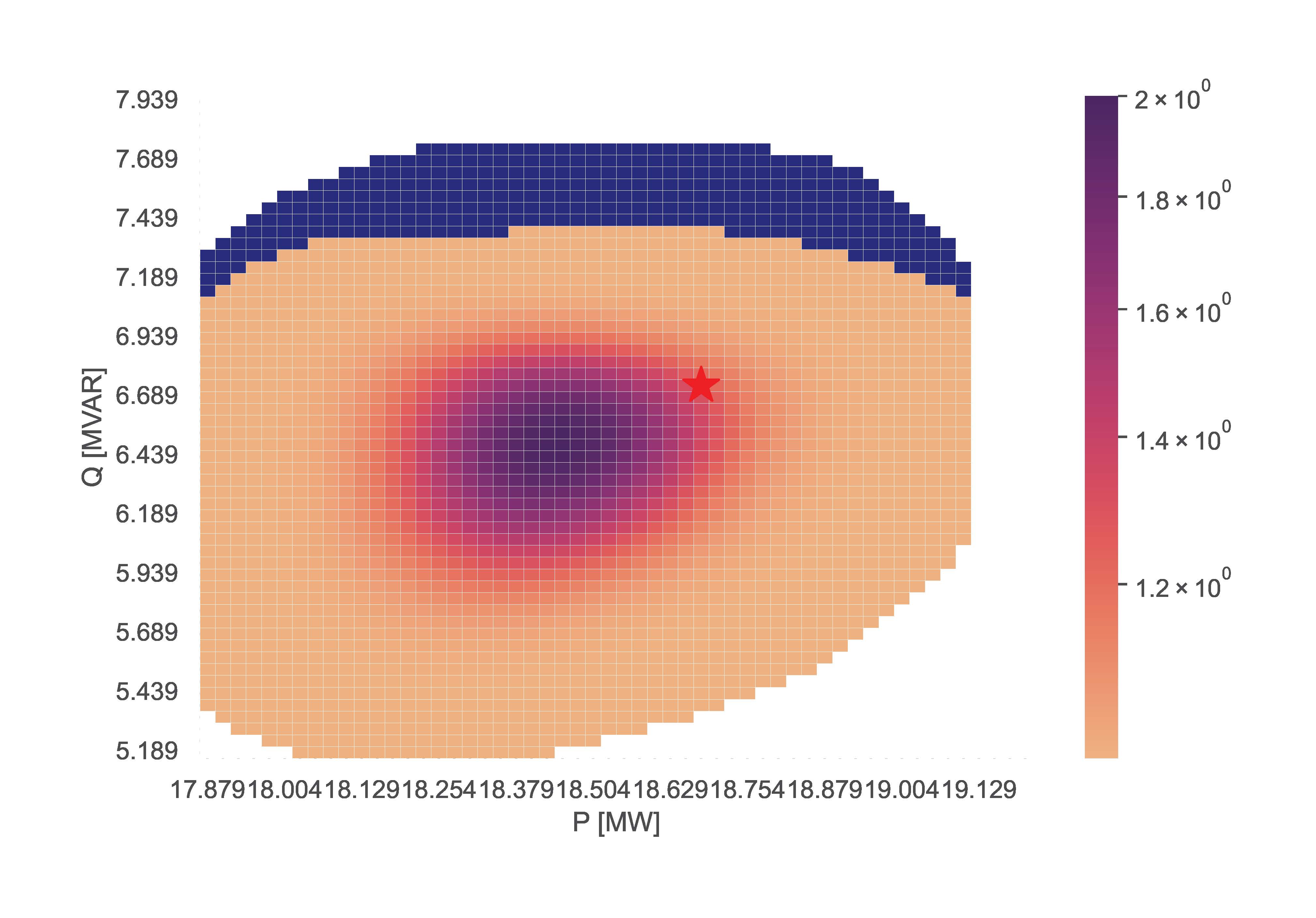
This section showcases the function merging FSPs using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm. For this functionality, the max_fsps input determines the maximum FSPs for which a network component can be sensitive before merging their flexibility. The example line is:
TCP.tc_plus_merge(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', fsp_load_indices=[1, 2, 3], dp=0.025, dq=0.05, fsp_dg_indices=[1, 2, 3], max_fsps=5)
The resulting figure is:
IV.F) TensorConvolution+ Adapt
This section showcases the function storing information using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm, and then uses the stored information to adapt flexibility area for altered operating conditions.
# Define the consistent FSPs for the storing and adapting functions
fsp_load_indices = [1, 2, 3]
fsp_dg_indices = [1, 2, 3]
# Estimate the FA and store the relevant information for adaptation
TCP.tc_plus_save_tensors(net_name='MV Oberrhein0', fsp_load_indices=fsp_load_indices, dp=0.05, dq=0.1, fsp_dg_indices=fsp_dg_indices)
# Modify the network operating conditions
net, net_tmp = pn.mv_oberrhein(separation_by_sub=True)
net.load['sn_mva'] = list(net.load['p_mw'].pow(2).add(net.load['q_mvar'].pow(2)).pow(0.5))
net.load['scaling'] = [1 for i in range(len(net.load))]
net.sgen['scaling'] = [1 for i in range(len(net.sgen))]
net.switch['closed'] = [True for i in range(len(net.switch))]
net = fix_net(net) # This function is included in the appendix
rng = np.random.RandomState(212)
net, rng = rand_resample(net, fsp_load_indices, fsp_dg_indices, rng, 0.05, 0.01, 0.05, 0.01) # This function is also included in the appendix
# Adapt the FA using the locally stored information
TCP.tc_plus_adapt(net=net, fsp_load_indices=fsp_load_indices, fsp_dg_indices=fsp_dg_indices)
# Estimate the FA without adapting to compare with the above adapted result
TCP.tc_plus(net=net, fsp_load_indices=fsp_load_indices, fsp_dg_indices=fsp_dg_indices, dp=0.05, dq=0.1)
The resulting figures for the stored, adapted and validated flexibility areas are:
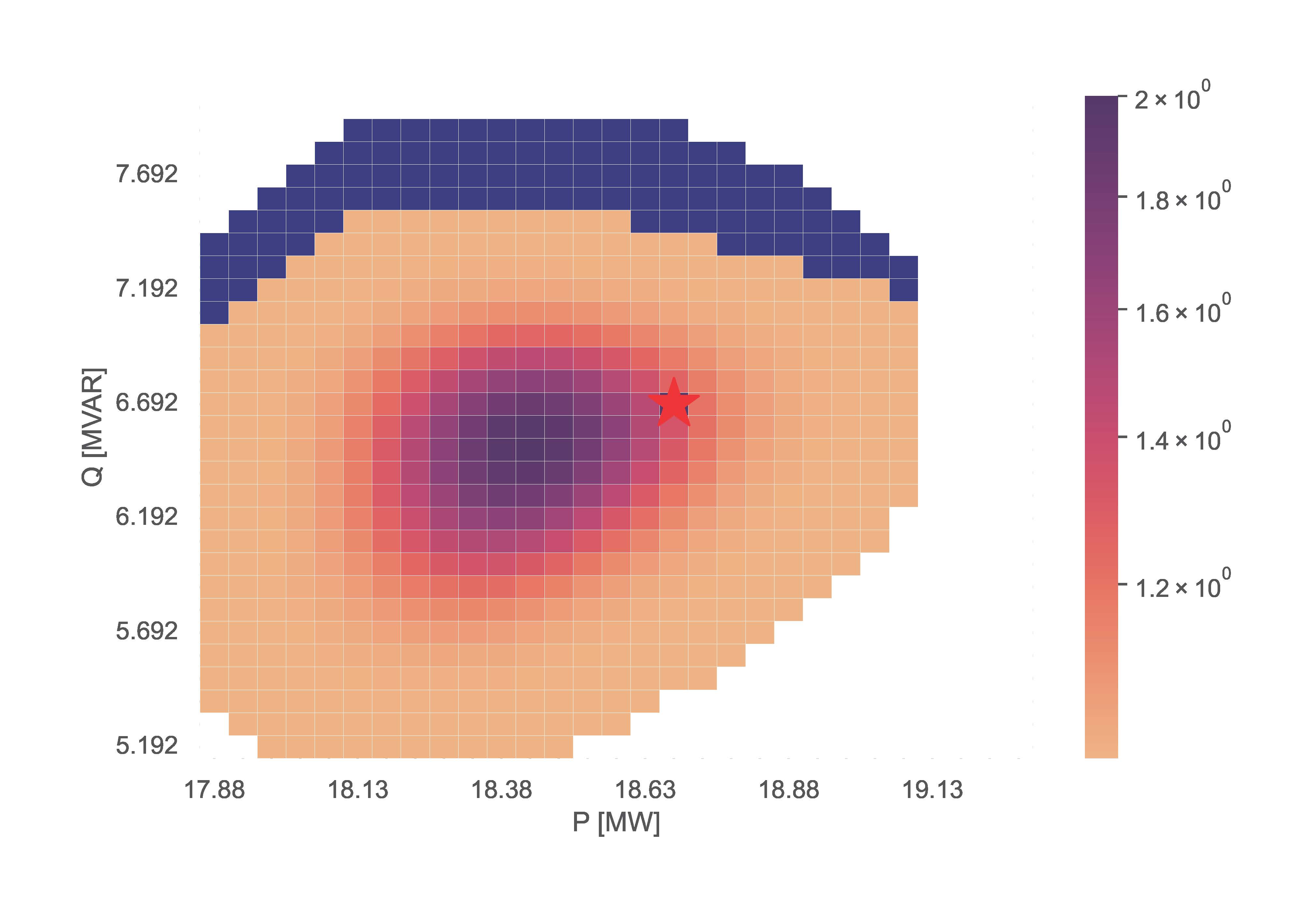
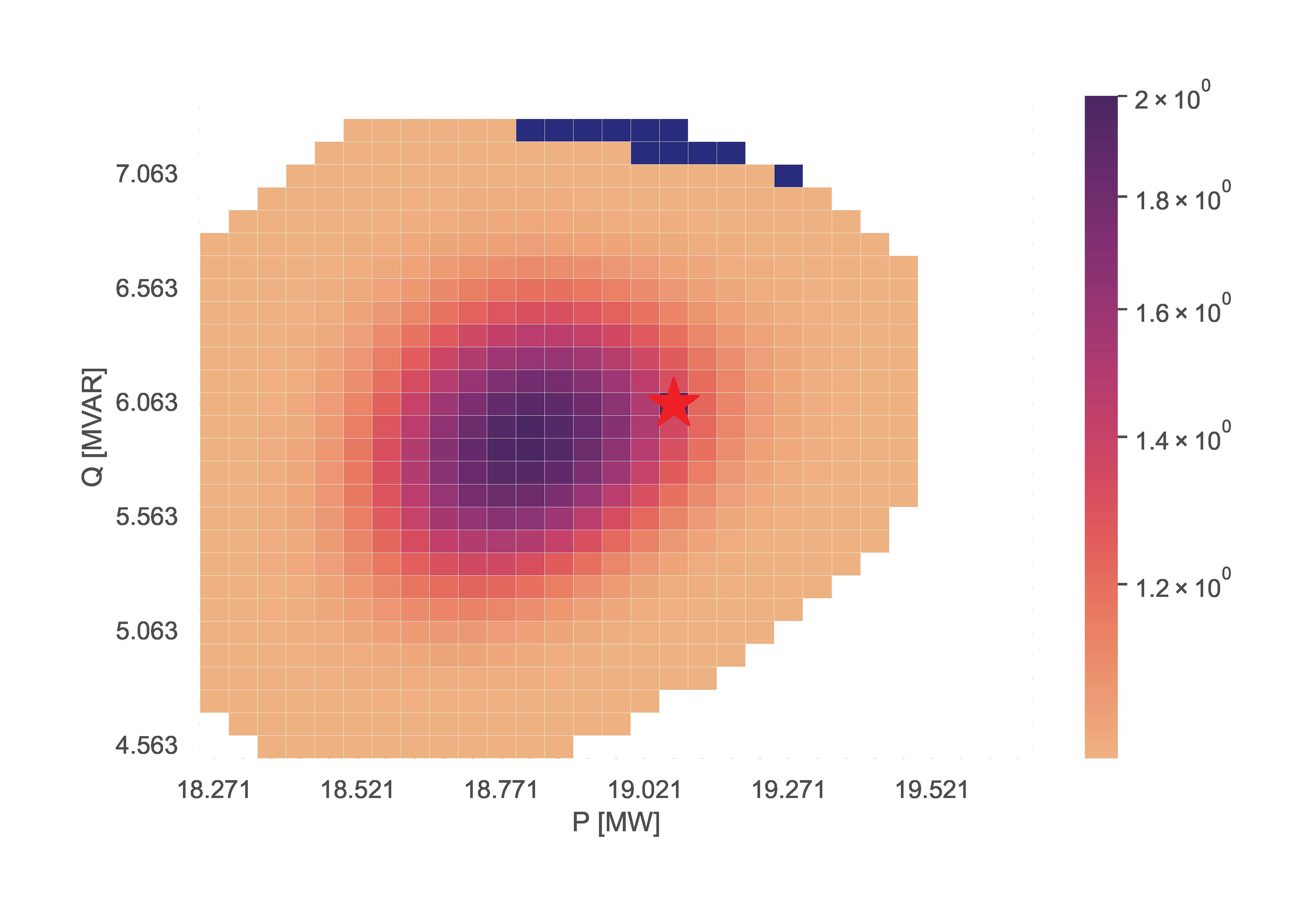

V. Functions
Package Functionalities
This Python Script includes all functions of the developed package.
- FA_Estimator.exhaustive_pf(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', dp: float = 0.05, dq: float = 0.05, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, non_linear_fsps: list = [], fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0})
Package Function to run the exhaustive power flow algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
dp (float) – step size in active power (optional). Default=0.05.
dq (float) – step size in reactive power (optional). Default=0.05.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
non_linear_fsps (list) – indices of non linear_fsps, offering 2 setpoints (optional). Default=[].
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
- FA_Estimator.monte_carlo_pf(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, no_samples: int = 10000, distribution: str = 'Hard', non_linear_fsps: list = [], fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0})
Package Function to run the Monte Carlo based power flow algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
no_samples (int) – number of samples for power flows (optional). Default=1000.
distribution (str) – distribution used for generated samples for power flows (optional). Default=’Hard’.
non_linear_fsps (list) – indices of non linear_fsps, offering 2 setpoints (optional). Default=[].
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
- FA_Estimator.opf(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Cigre', opf_step: float = 0.1, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 101})
Package function to run the optimal power flow algorithm. This function has convergence issues, where only Cigre MV network converges and without transformer loading contraints.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Cigre’, currently the only converging option.
opf_step (float) – OPF step size. Default=0.1.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 101}.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot is stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
- FA_Estimator.tc_plus(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', dp: float = 0.05, dq: float = 0.05, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, l_sens: float = 1, v_sens: float = 0.001, non_linear_fsps: list = [], fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0}, flex_shape: str = 'Smax')
Package Function to run the TensorConvolution+ algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – Pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – Network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
dp (float) – step size in active power (optional). Default=0.05.
dq (float) – step size in reactive power (optional). Default=0.05.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
l_sens (float) – loading sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=1.
v_sens (float) – voltage sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=0.001.
non_linear_fsps (list) – indices of non linear_fsps, offering 2 setpoints (optional). Default=[].
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
flex_shape (dict) – Shape of flexibility from service providers. To change the shape for different resources, or change the shape for all resources, plase create a new function in place of conv_profile_creation(). Currently supported shapes: “Smax”: resource outputs cannot exceed the maximum apparent power (semi-oval shape), “PQmax”: resource active and reactive power individually cannot exceed maximum apparent power (rectangle shape). Default=”Smax”.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
- FA_Estimator.tc_plus_adapt(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, non_linear_fsps: list = [], fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0})
Package Function to run the TensorConvolution+ algorithm and adapt from stored tensors for previous OCs.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – Pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – Network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
dp (float) – step size in active power (optional). Default=0.05.
dq (float) – step size in reactive power (optional). Default=0.05.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
non_linear_fsps (list) – not tested for this modality. Kept as input for future expansion. Default=[].
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (must be the exact same as the scenario it adapts from). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (must be the exact same as the scenario it adapts from). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
- FA_Estimator.tc_plus_merge(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', dp: float = 0.05, dq: float = 0.05, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, l_sens: float = 1, v_sens: float = 0.001, fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0}, flex_shape: str = 'Smax', max_fsps: int = -1)
Package Function to run the TensorConvolution+ algorithm but merge FSPs for network components that are sensitive to more than ‘max_fsps’ FSPs (to solve possible memory issues but possibly reduce accuracy).
- param net:
Pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
- type net:
pp.networks
- param net_name:
Network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
- type net_name:
str
- param dp:
step size in active power (optional). Default=0.05.
- type dp:
float
- param dq:
step size in reactive power (optional). Default=0.05.
- type dq:
float
- param max_curr_per:
network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
- type max_curr_per:
int
- param max_volt_pu:
network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
- type max_volt_pu:
float
- param min_volt_pu:
network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
- type min_volt_pu:
float
- param l_sens:
loading sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=1.
- type l_sens:
float
- param v_sens:
voltage sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=0.001.
- type v_sens:
float
- param fsp_load_indices:
indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
- type fsp_load_indices:
list
- param fsp_dg_indices:
indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
- type fsp_dg_indices:
list
- param scenario_type:
Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
- type scenario_type:
dict
- param flex_shape:
Shape of flexibility from service providers. To change the shape for different resources, or change the shape for all resources, plase create a new function in place of conv_profile_creation(). Currently supported shapes: “Smax”: resource outputs cannot exceed the maximum apparent power (semi-oval shape), “PQmax”: resource active and reactive power individually cannot exceed maximum apparent power (rectangle shape). Default=”Smax”.
- type flex_shape:
dict
- param max_fsps:
Number of FSPs to allow for each component’s sensitivity before merging. Default=-1 would take maximum FSPs as the input FSPs -1 (merging at most 2 FSPs into 1).
- type max_fsps:
int
- return:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- rtype:
None
- FA_Estimator.tc_plus_save_tensors(net=None, net_name: str = 'MV Oberrhein0', dp: float = 0.05, dq: float = 0.05, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95, l_sens: float = 1, v_sens: float = 0.001, non_linear_fsps: list = [], fsp_load_indices: list = [], fsp_dg_indices: list = [], scenario_type: dict = {'name': 'CS', 'no.': 0}, flex_shape: str = 'Smax')
Package Function to run the TensorConvolution+ algorithm and save the tensors during estimation.
- Parameters:
net (pp.networks) – Pandapower network (optional). Default=None.
net_name (str) – Network name (optional, only used if network is not given). Default=’MV Oberrhein0’.
dp (float) – step size in active power (optional). Default=0.05.
dq (float) – step size in reactive power (optional). Default=0.05.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
l_sens (float) – loading sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=1.
v_sens (float) – voltage sensitivity threshold (optional). Default=0.001.
non_linear_fsps (list) – indices of non linear_fsps, offering 2 setpoints (optional). Default=[].
fsp_load_indices (list) – indices of load FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
fsp_dg_indices (list) – indices of DG FSPs (optional, but at least one of fsp_load_indices or fsp_dg_indices should be non-empty). Default=[].
scenario_type (dict) – Scenario for network settings (e.g.CS=closed switches, only used if net is None). Default={“name”: ‘CS’, “no.”: 0}.
flex_shape (dict) – Shape of flexibility from service providers. To change the shape for different resources, or change the shape for all resources, plase create a new function in place of conv_profile_creation(). Currently supported shapes: “Smax”: resource outputs cannot exceed the maximum apparent power (semi-oval shape), “PQmax”: resource active and reactive power individually cannot exceed maximum apparent power (rectangle shape). Default=”Smax”.
- Returns:
Flexibility area plot and csv of dataframe are stored locally. The function returns nothing.
- Return type:
None
Convolution Simulations
This Python Script includes all functions applying tensor convolutions to estimate flexibility areas.
- conv_simulations.adaptable_new_op(net, init_pcc_pq, minmax_v=[0.95, 1.05], max_l=100)
Calculate FA using previous FA estimation for different operating conditions. This function calculates the flexibility area (FA) using previous FA estimation for different operating conditions.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
init_pcc_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) of the PCC.
minmax_v (list[float, float]) – The scenario network voltage constraints.
max_l (float) – The scenario network loading constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility area (FA), the uncertainty including flexibility area, the reachable area, the binary flexibility area, the p index of initial operating point, the q index of initial operating point, a string on the simulation duration, extra info depending on scenario.
- Return type:
pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, float, float, str, pandas.Dataframe
- conv_simulations.combine_shapes(shapes, pq_steps)
Combine the feasible regions for different discontinuous area setpoints. This function combines the feasible regions for different discontinuous area setpoints.
- Parameters:
shapes (list[str]) – The flexibility regions for different setpoints of the non-linear FSP.
pq_steps (numpy.ndarray/list) – Non linear FSPs P,Q setpoints.
- Returns:
The combined flexibility region.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.combine_shapes_const_flex(shapes, pq_steps, flex)
Combine the feasible regions for different discontinuous area setpoints, in case where no network constraint can be reached. This function combines the feasible regions for different discontinuous area setpoints, in case where no network constraint can be reached.
- Parameters:
shapes (list[str]) – The flexibility regions for different setpoints of the non-linear FSP.
pq_steps (numpy.ndarray/list) – Non linear FSPs P,Q setpoints.
flex (numpy.ndarray/list) – Flexibility region linear FSPs.
- Returns:
The combined flexibility region.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.create_mat_dict_incl_delta(result_dict, dp, dq, non_lin_fsp, init_pq)
Create matrices, dictionaries, and axes from a result dictionary including delta values. This function takes a dictionary of results and generates matrices, dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q) with and without delta values. It also includes non-linear power systems for the given keys.
- Parameters:
result_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing result data.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
non_lin_fsp (list) – A list of keys corresponding to non-linear power systems.
init_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q).
- Returns:
The resulting power matrix (PQ), dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q) without delta, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q) with delta, and an uncertainty matrix for feasibility.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, dict, list, list, list, list, dict
- conv_simulations.create_mat_dict_order(result_dict, dp, dq, small_fsps=[])
Create matrices and dictionaries from a result dictionary using PyTorch tensors. This function takes a dictionary of results and generates matrices and dictionaries based on the provided dp and dq values. It performs convolution operations on selected matrices and returns the resulting matrices, dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q), and the order of keys used in the convolution.
- Parameters:
result_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing result data.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
small_fsps (list[str]) – A list of keys corresponding to small flexible power systems.
- Returns:
The resulting power matrix (PQ), dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q), and the order of keys used in convolution.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, dict, list, list, list
- conv_simulations.create_mat_dict_tensor(result_dict, dp, dq, small_fsps=[])
Create matrices and dictionaries from a result dictionary using PyTorch tensors. This function takes a dictionary of results and generates matrices and dictionaries based on the provided dp and dq values. It performs convolution operations on selected matrices and returns the resulting matrices, dictionaries, and axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q). Additionally, it calculates the uncertainty factor (unc_fa).
- Parameters:
result_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing result data.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
small_fsps (list[str]) – A list of keys corresponding to small flexible power systems.
- Returns:
The resulting power matrix (PQ), dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q), and the uncertainty factor matrix (unc_fa).
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, dict, list, list, numpy.ndarray
- conv_simulations.create_mat_dict_tensorv2(result_dict, dp, dq)
Create matrices and dictionaries from a result dictionary using PyTorch tensors. This function takes a dictionary of results and generates matrices, dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q), and initialization IDs based on the provided dp and dq values.
- Parameters:
result_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing result data.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
- Returns:
The resulting power matrix (PQ), dictionaries, axes for power (P) and reactive power (Q), the initialization IDs, and an uncertainty matrix for feasibility.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, dict, list, list, dict
- conv_simulations.create_multi_small_fsp_fas(prof_dict, dp, dq, init_fsp_pq)
Create a multi-flexibility area (MFA) by combining small feasible space profiles. This function combines multiple small feasible space profiles into a single multi-flexibility area (MFA) using convolution.
- Parameters:
prof_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing small feasible space profiles.
dp (float) – The step size for active power (P).
dq (float) – The step size for reactive power (Q).
init_fsp_pq (dict) – Initial values for active power (P) and reactive power (Q) for each profile.
- Returns:
The multi-flexibility area (MFA) obtained by combining small feasible space profiles.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- conv_simulations.df_to_mat_tensor_scaled_and_init(df, dp, dq)
Take dataframes of power flow results and create matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions. This function takes dataframes of power flow results and creates matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – Dataframe with power flow results.
dp (float) – Resolution in dp.
dq (float) – Resolution in dq.
- Returns:
The result dictionary, p axis and q axis.
- Return type:
dict, np.array, np.array
- conv_simulations.df_to_mat_tensor_torch(df, dp, dq)
Take dataframes of power flow results and create matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions. This function takes dataframes of power flow results and creates matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – Dataframe with power flow results.
dp (float) – Resolution in dp.
dq (float) – Resolution in dq.
- Returns:
The result dictionary, p axis and q axis.
- Return type:
dict, np.array, np.array
- conv_simulations.df_to_mat_tensor_torchv2(df, dp, dq)
Take dataframes of power flow results and create matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions. This function takes dataframes of power flow results and creates matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – Dataframe with power flow results.
dp (float) – Resolution in dp.
dq (float) – Resolution in dq.
- Returns:
The result dictionary, p axis and q axis.
- Return type:
dict, np.array, np.array
- conv_simulations.enhance_multi_big_fa(fa, times=5.0)
Enhance the size of a multi-flexibility area (MFA) using bilinear interpolation. This function enhances the size of a multi-flexibility area (MFA) by a specified factor using bilinear interpolation.
- Parameters:
fa (numpy.ndarray) – The multi-flexibility area (MFA) to be enhanced.
times (float, optional) – The enhancement factor (default is 5.0).
- Returns:
The enhanced multi-flexibility area (MFA).
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- conv_simulations.find_value_close2list(lst, voi)
Find the index and closest value in a list to a specified value. This function searches for the index and value in the input list lst that is closest to the specified value voi. It iterates through the list and calculates the absolute difference between each element and voi to find the closest match.
- Parameters:
lst (list[float]) – The list to search for the closest value.
voi (float) – The value to find the closest match for.
- Returns:
The index of the closest value in the list and the closest value itself.
- Return type:
int, float
- conv_simulations.get_bus_line_and_trafo_names(net)
Get names of buses, lines, and transformers in a power distribution network. This function extracts and returns the names of buses, lines, and transformers from the provided pandapowerNet object.
- Parameters:
net (pandapowerNet) – A pandapowerNet object representing a power distribution network.
- Returns:
A list of bus names, line names, and transformer names.
- Return type:
list[str], list[str], list[str]
- conv_simulations.get_delta(df, dp, dq, init_pq)
Take dataframes of power flow results and create matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions, for non-linear FSPS. This function takes dataframes of power flow results and creates matrices of feasible regions, sensitivities for tensor convolutions, for non-linear FSPS.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – Dataframe with power flow results.
dp (float) – Resolution in dp.
dq (float) – Resolution in dq.
init_pq (list[float, float]) – Initial P,Q values.
- Returns:
The result list, p axis, q axis, and binary matrix.
- Return type:
list, np.array, np.array, np.array
- conv_simulations.get_init_net_state(net)
Calculate initial network component voltage and loading values. This function calculates the initial network component voltage and loading values.
- Returns:
Two dictionaries containing the initial voltage magnitude for buses, and loading for lines/transformers.
- Return type:
dict, dict
- conv_simulations.get_multi_conv_key_adapting_new_op(comp, bus_nm, init_v, init_load, min_v, max_v)
Calculate flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs using previous FA estimation for different operating conditions. This function calculates the flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs using previous FA estimation for different operating conditions.
- Parameters:
comp (str) – The distribution network component name (e.g.bus 1).
bus_nm (list[str]) – Distribution network bus names.
init_v (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial voltage magnitudes of network buses.
init_load (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial loading of network lines/transformers.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility region from FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_conv_key_saving(fsps_of_comp, mat_dicts, comp, bus_nm, init_v, init_load, max_v=1.05, min_v=0.95)
Calculate flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, perform TTD on the tensors and save them locally.
This function calculates the flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, perform TTD on the tensors and save them locally.
- Parameters:
fsps_of_comp (list[str]) – The FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
mat_dicts (dict) – The dictionary of power flow sensitivities from each FSP per component.
comp (str) – The distribution network component name (e.g.bus 1).
bus_nm (list[str]) – Distribution network bus names.
init_v (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial voltage magnitudes of network buses.
init_load (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial loading of network lines/transformers.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility region from FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_conv_key_with_delta(fsps_of_comp, mat_dicts, comp, bus_nm, init_v, init_load, comp_non_lin_fsp, pq_steps, max_v=1.1, min_v=0.9)
Calculate flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, while having discrete FSPs. This function calculates the flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, while having discrete FSPs.
- Parameters:
fsps_of_comp (list[str]) – The FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
mat_dicts (dict) – The dictionary of power flow sensitivities from each FSP per component.
comp (str) – The distribution network component name (e.g.bus 1).
bus_nm (list[str]) – Distribution network bus names.
init_v (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial voltage magnitudes of network buses.
init_load (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial loading of network lines/transformers.
comp_non_lin_fsp (list) – Non linear FSPs for which the component is sensitive.
pq_steps (numpy.ndarray/list) – Non linear FSPs P,Q setpoints.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility region from FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_conv_torch(fsps_of_comp, mat_dicts, comp, bus_nm, init_v, init_load, max_v=1.05, min_v=0.95)
Calculate flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs. This function calculates the flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs.
- Parameters:
fsps_of_comp (list[str]) – The FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
mat_dicts (dict) – The dictionary of power flow sensitivities from each FSP per component.
comp (str) – The distribution network component name (e.g.bus 1).
bus_nm (list[str]) – Distribution network bus names.
init_v (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial voltage magnitudes of network buses.
init_load (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial loading of network lines/transformers.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility region from FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_conv_torch_split(fsps_of_comp, mat_dicts, comp, bus_nm, init_v, init_load, sim_dict, init_ids, max_v=1.05, min_v=0.95, no_max=5)
Calculate flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, but merge FSPs until maximum fsps are no_max-1. This function calculates the flexibility region for component from sensitive FSPs, but merge FSPs until maximum fsps are no_max-1.
- Parameters:
fsps_of_comp (list[str]) – The FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
mat_dicts (dict) – The dictionary of power flow sensitivities from each FSP per component.
comp (str) – The distribution network component name (e.g.bus 1).
bus_nm (list[str]) – Distribution network bus names.
init_v (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial voltage magnitudes of network buses.
init_load (numpy.ndarray/list) – Initial loading of network lines/transformers.
sim_dict (dictionary) – Estimated electrical dinstance per FSP pair.
init_ids (dictionary) – Initial P,Q values per FSP.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
no_max (int) – The maximum+1 FSPs that can be accounted for in the tensors.
- Returns:
The flexibility region from FSPs in which the component is sensitive.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_result_for_0_effective(non_effective_fsps, mat_dicts)
Estimate flexibility area if no component can reach its constraint. This function estimated flexibility area, in case where no network constraint can be reached.
- Parameters:
non_effective_fsps (list[str]) – The FSP names.
mat_dicts (dict) – The power flow results.
- Returns:
The flexibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_multi_uncertain_fa(pq_mat, large_fa, small_prof_dict, dp, dq, init_fsp_pq, p_axes, q_axes)
Calculate multiple uncertain feasibility areas from given power matrices. This function calculates multiple uncertain feasibility areas (UFAs) from the given power matrices. It uses both small and large feasibility areas to create UFAs and scales them accordingly.
- Parameters:
pq_mat (numpy.ndarray) – The power matrix representing the feasibility area.
large_fa (numpy.ndarray) – The large feasibility area used for enhancement.
small_prof_dict (dict) – A dictionary containing small feasibility profiles.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
init_fsp_pq (dict) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) for small feasibility profiles.
p_axes (numpy.ndarray) – The power (P) axes for matrix generation.
q_axes (numpy.ndarray) – The reactive power (Q) axes for matrix generation.
- Returns:
The scaled uncertain feasibility area (UFA), the scaled safe area, the scaled uncertain feasibility area with ones, the new power (P) axes for the large feasibility area, and the new reactive power (Q) axes for the large feasibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray
- conv_simulations.get_new_conv_axes2(list_of_rows, list_of_columns, conv_q_len, conv_p_len, q, p)
Combine axes per FSP to get the final flexibility area axes. This function combines axes per FSP to get the final flexibility area axes.
- Parameters:
list_of_rows (list) – Row axes from all FSPs.
list_of_columns (list) – Column axes from all FSPs.
conv_q_len (int) – Convolution result (reachability) height length in pixels.
conv_p_len (int) – Convolution result (reachability) weight length in pixels.
q (float) – The network PCC initial q.
p (float) – The network PCC initial p.
- Returns:
The flexibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_non_effective_multi_conv(non_effective_fsps, effective_conv, mat_dicts)
Estimate flexibility area by convolving non-effective fsps with the region from the effective fsps. This function estimates flexibility area by convolving non-effective fsps with the region from the effective fsps.
- Parameters:
non_effective_fsps (list[str]) – The non-effective FSP names.
effective_conv (numpy.array) – The effective FSP flexibility area.
mat_dicts (dict) – The power flow results.
- Returns:
The flexibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_non_effective_multi_conv_with_delta(non_effective_fsps, effective_conv, mat_dicts, non_eff_non_lin_fsps, pq_steps)
Estimate flexibility area by convolving non-effective fsps with the region from the effective fsps, also accounting for non-effective non-linear FSPs. This function estimates flexibility area by convolving non-effective fsps with the region from the effective fsps.
- Parameters:
non_effective_fsps (list[str]) – The non-effective FSP names.
effective_conv (numpy.array) – The effective FSP flexibility area.
mat_dicts (dict) – The power flow results.
non_eff_non_lin_fsps (list[str]) – The non-effective non-linear FSP names.
pq_steps (dict) – The P,Q setpoints of the non-effective non-linear FSP names.
- Returns:
The flexibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.get_result_for_0_effective_with_delta(final_flex, non_lin_eff_fsp_per_comp, non_lin_ineff_fsp_per_comp, pq_steps, bus_nm, init_v, init_l, mat_dicts, max_v, min_v)
Estimate flexibility area if no component can reach its constraint, and non-linear FSPs exist. This function estimated flexibility area, in case where no. network constraint can be reached.
- Parameters:
final_flex (numpy.array) – The linear FSP flexibility area.
non_lin_eff_fsp_per_comp (dict) – The non-linear but effective FSP names.
non_lin_ineff_fsp_per_comp (dict) – The non-linear non-effective FSP names.
pq_steps (dict) – The P,Q setpoints of the non-effective non-linear FSP names.
bus_nm (list[str]) – The network bus names.
init_v (dict) – The network bus initial voltage magnitudes.
init_l (dict) – The network line/transformer initial loading.
mat_dicts (dict) – The power flow results.
max_v (dict) – The network constraint maximum voltage magnitudes.
min_v (dict) – The network constraint minimum voltage magnitudes.
- Returns:
The flexibility area.
- Return type:
numpy.array
- conv_simulations.numpy_tensor_conv_simulations_saving(net, pq_profiles, dp, dq, init_pcc_pq, small_fsp_prof, comp_fsp_v_sens=0.001, comp_fsp_l_sens=0.1, min_max_v=[0.95, 1.05], max_l=100)
Calculate FA using Tensors and Convolutions, while saving the tensors (after TTD) to adapt FA in other operating conditions. This function calculates the flexibility area (FA) using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm while saving the tensors (after TTD) to adapt FA in other operating conditions.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
pq_profiles (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the DG.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
init_pcc_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) of the PCC.
small_fsp_prof (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the small DG.
comp_fsp_v_sens (float) – The scenario voltage sensitivity.
comp_fsp_l_sens (float) – The scenario loading sensitivity.
min_max_v (list[float, float]) – The scenario network voltage constraints.
max_l (float) – The scenario network loading constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility area (FA), the uncertainty including flexibility area, the reachable area, the binary flexibility area, the p index of initial operating point, the q index of initial operating point, a string on the simulation duration, extra info depending on scenario.
- Return type:
pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, float, float, str, pandas.Dataframe
- conv_simulations.numpy_tensor_conv_simulations_with_delta(net, pq_profiles, dp, dq, init_pcc_pq, small_fsp_prof, non_lin_fsp=[], comp_fsp_v_sens=0.001, comp_fsp_l_sens=1, max_v=1.1, min_v=0.9, max_l=100)
Calculate FA using Tensors and Convolutions, when at least 1 fsp can only shift in certain setpoints. This function calculates the flexibility area (FA) using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
pq_profiles (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the DG.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
init_pcc_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) of the PCC.
small_fsp_prof (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the small DG.
non_lin_fsp (list) – The non linear DG.
comp_fsp_v_sens (float) – The scenario voltage sensitivity.
comp_fsp_l_sens (float) – The scenario loading sensitivity.
max_v (float) – The scenario network maximum voltage constraints.
min_v (float) – The scenario network minimum voltage constraints.
max_l (float) – The scenario network loading constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility area (FA), the uncertainty including flexibility area, the reachable area, the binary flexibility area, the p index of initial operating point, the q index of initial operating point, a string on the simulation duration, extra info depending on scenario.
- Return type:
pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, float, float, str, pandas.Dataframe
- conv_simulations.profiles_to_mat(profiles, dp, dq, init_fsp_pq)
Take dataframes of power flow results and create matrices of feasible regions. This function takes dataframes of power flow results and creates matrices of feasible regions.
- Parameters:
profiles (pandas.dataframe) – Dataframe with power flow results.
dp (float) – Resolution in dp.
dq (float) – Resolution in dq.
init_fsp_pq (list[float, float]) – Initial P,Q values for FSPs.
- Returns:
Matrix of shifts sensitivities.
- Return type:
np.array
- conv_simulations.reduce_multi_fa_small(fa, times=0.5)
Reduce the size of a multi-flexibility area (MFA) using bi-linear interpolation. This function reduces the size of a multi-flexibility area (MFA) by a specified factor using bi-linear interpolation.
- Parameters:
fa (numpy.ndarray) – The multi-flexibility area (MFA) to be reduced.
times (float, optional) – The reduction factor (default is 0.5).
- Returns:
The reduced multi-flexibility area (MFA).
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- conv_simulations.run_all_tensor_flex_areas(net, pq_profiles, bus_nm, line_nm, trafo_nm, init_v, init_load)
Run power flows for all FSP setpoints given. This function runs power flows for given FSP setpoints.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – Distribution network.
pq_profiles (numpy.array/list) – Sapled setpoints per FSP.
bus_nm (list) – Network bus names.
line_nm (list) – Network line names.
trafo_nm (list) – Network transformer names.
init_v (dict) – The network initial voltage magnitudes for all buses.
init_load (dict) – The network initial loading for all lines and transformers.
- Returns:
The result dictionary, standard deviation information, and duration.
- Return type:
dict, dict, float
- conv_simulations.split_lin_from_non_lin(comp_dict, non_lin_fsp)
Split linear from non-linear FSPs. This function splits linear from non-linear FSPs.
- Returns:
Two dictionaries containing continuous capabilities FSPs, and the discrete (only full curtailment) capabilities FSPs.
- Return type:
dict, dict
- conv_simulations.torch_tensor_conv_large_simulations(net, pq_profiles, dp, dq, init_pcc_pq, small_fsp_prof, dist_dicts, comp_fsp_v_sens=0.001, comp_fsp_l_sens=1, min_max_v=[0.95, 1.05], max_l=100, no_max=5)
Calculate FA using Tensors and Convolutions, but merge FSPs in components who have no_max or more FSPs sensitivities, until maximum sensitive FSPs are no_max-1 per component. This function calculates the flexibility area (FA) using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
pq_profiles (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the DG.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
init_pcc_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) of the PCC.
small_fsp_prof (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the small DG.
dist_dicts (dict) – The dinstance between each FSP pair.
comp_fsp_v_sens (float) – The scenario voltage sensitivity.
comp_fsp_l_sens (float) – The scenario loading sensitivity.
min_max_v (list[float, float]) – The scenario network voltage constraints.
max_l (float) – The scenario network loading constraints.
no_max (int) – The scenario maximum+1 FSPs per component.
- Returns:
The flexibility area (FA), the uncertainty including flexibility area, the reachable area, the binary flexibility area, the p index of initial operating point, the q index of initial operating point, a string on the simulation duration, extra info depending on scenario.
- Return type:
pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, float, float, str, pandas.Dataframe
- conv_simulations.torch_tensor_conv_simulations(net, pq_profiles, dp, dq, init_pcc_pq, small_fsp_prof, comp_fsp_v_sens=0.001, comp_fsp_l_sens=0.1, min_max_v=[0.95, 1.05], max_l=100)
Calculate FA using Tensors and Convolutions. This function calculates the flexibility area (FA) using the TensorConvolution+ algorithm.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
pq_profiles (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the DG.
dp (float) – The power resolution (dp) for matrix generation.
dq (float) – The reactive power resolution (dq) for matrix generation.
init_pcc_pq (tuple) – Initial values for power (P) and reactive power (Q) of the PCC.
small_fsp_prof (numpy.ndarray/list) – The sampled p,q setpoints for the small DG.
comp_fsp_v_sens (float) – The scenario voltage sensitivity.
comp_fsp_l_sens (float) – The scenario loading sensitivity.
min_max_v (list[float, float]) – The scenario network voltage constraints.
max_l (float) – The scenario network loading constraints.
- Returns:
The flexibility area (FA), the uncertainty including flexibility area, the reachable area, the binary flexibility area, the p index of initial operating point, the q index of initial operating point, a string on the simulation duration, extra info depending on scenario.
- Return type:
pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, pandas.Dataframe, float, float, str, pandas.Dataframe
- conv_simulations.update_conv_pqs(net, fsp_idx, fsp_type, profile)
Update the FSPs to perform power flows. This function updates the FSPs to perform power flows.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – The distribution network.
fsp_idx (int) – The index value of the FSP in the network.
fsp_type (str) – The type of the FSP in the network.
profile (list[float, float]) – The p,q new setpoints for the FSP.
- Returns:
Updated network.
- Return type:
pandapower.network
Monte Carlo
This Python Script includes all functions applying Monte-Carlo based simulations.
- monte_carlo.all_pf_simulations(settings, net, pq_profiles)
main function running all power flow simulations based on which FSP types will be used.
- Parameters:
settings (object) – Information of the json file.
net (pandapower.network) – Network on which the simulations will be performed.
pq_profiles (list) – P and Q values for each FSP for each iteration in the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Returns:
feasible P, feasible Q, infeasible P, infeasible Q, duration of simulations [s], FSP PQ values for the feasible y, FSP PQ values for the infeasible y.
- Return type:
list, list, list, list, float, list, list
- monte_carlo.get_fsp_ids(fsp, dataframe)
Get ID of fsp number.
- Parameters:
fsp (list) – fsp numbers.
dataframe (pandas.dataframe) – fsp information.
- Returns:
ids of fsps.
- Return type:
list
- monte_carlo.run_all_samples(settings, net, pq_profiles)
Run all power flows for scenarios where only DG are used as FSP.
- Parameters:
settings (object) – information of the json file.
net (pandapower.network) – Network on which the simulations will be performed.
pq_profiles (list) – P and Q values for each FSP for each iteration in the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Returns:
feasible P, feasible Q, infeasible P, infeasible Q, duration of simulations [s], FSP PQ values for the feasible y, FSP PQ values for the infeasible y.
- Return type:
list, list, list, list, float, list, list
- monte_carlo.run_all_samples_wl(settings, net, pq_profiles)
Run all power flows for scenarios where loads are included in the FSP.
- Parameters:
settings (object) – information of the json file.
net (pandapower.network) – network on which the simulations will be performed.
pq_profiles (list) – P and Q values for each FSP for each iteration in the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Returns:
feasible P, feasible Q, infeasible P, infeasible Q, duration of simulations [s], FSP PQ values for the feasible y, FSP PQ values for the infeasible y.
- Return type:
list, list, list, list, float, list, list
- monte_carlo.run_uc6(settings, net, pq_profiles)
Run all power flows for scenarios where loads are included in the FSP.
- Parameters:
settings (object) – information of the json file.
net (pandapower.network) – network on which the simulations will be performed.
pq_profiles (list) – P and Q values for each FSP for each iteration in the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Returns:
feasible P, feasible Q, infeasible P, infeasible Q, duration of simulations [s], FSP PQ values for the feasible y, FSP PQ values for the infeasible y.
- Return type:
list, list, list, list, float, list, list
- monte_carlo.run_uc6_volts(settings, net, v_profiles)
Run all power flows for scenarios where loads are included in the FSP.
- Parameters:
settings (object) – information of the json file.
net (pandapower.network) – network on which the simulations will be performed.
pq_profiles (list) – P and Q values for each FSP for each iteration in the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Returns:
feasible P, feasible Q, infeasible P, infeasible Q, duration of simulations [s], FSP PQ values for the feasible y, FSP PQ values for the infeasible y.
- Return type:
list, list, list, list, float, list, list
Data Sampler
This Python Script includes all functions sampling FSP shifts.
- data_sampler.append_margin_profiles(pq_profiles, max_s, p, dp, dq, no_samples)
Add profiles for vertical shifts needed due to discretization.
- Parameters:
pq_profiles (list) – p,q values for the shifts.
max_s (float) – maximum apparent power of component.
p (float) – active power set-point.
dp (float) – resolution in active power shifts.
dq (float) – resolution in reactive power shifts.
no_samples (int) – number of samples.
- Returns:
new p,q profiles.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.check_margins(max_s, p, dp, dq, no_samples)
Check if new vertical shifts should be given due to the descritization.
- Parameters:
max_s (float) – maximum apparent power of component.
p (float) – active power set-point.
dp (float) – resolution in active power shifts.
dq (float) – resolution in reactive power shifts.
no_samples (int) – number of samples.
- Returns:
how many additional vertical shift samples are needed.
- Return type:
int
- data_sampler.combine_profiles(profiles, key_order_dg, key_order_load)
Combine profiles from DGs and Loads.
- Parameters:
profiles (list) – profiles generated for all (large) DGs.
key_order_dg (list) – order of DG names in profile.
key_order_load (list) – order of load names in profile.
- Returns:
Combined profiles from all FSPs.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.conv_profile_creation(dp, dq, net, services='DG Only', flexible_loads=[], flexible_dgs=[], non_linear_dgs=[])
Create profiles for convolution simulations.
- Parameters:
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
net (pandapower.network) – PandaPower network in which the simulations are performed.
services (str) – If FSPs are DG, Loads or both.
flexible_loads (list[int]) – Which Loads are considered FSPs.
flexible_dgs (list[int]) – Which DG are considered FSPs.
non_linear_dgs (list[int]) – Which FSP DGs are considered non-linear.
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each FSP, for all power flow simulations, the active and reactive power for each small FSP, the duration in seconds for the sample creations, the names of non-linear DGs.
- Return type:
list, list, float, list
- data_sampler.conv_profile_creation_sq(dp, dq, net, services='DG Only', flexible_loads=[], flexible_dgs=[], non_linear_dgs=[])
Create square shaped profiles for convolution simulations.
- Parameters:
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
net (pandapower.network) – PandaPower network in which the simulations are performed.
services (str) – If FSPs are DG, Loads or both.
flexible_loads (list[int]) – Which Loads are considered FSPs.
flexible_dgs (list[int]) – Which DG are considered FSPs.
non_linear_dgs (list[int]) – Which FSP DGs are considered non-linear.
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each FSP, for all power flow simulations, the active and reactive power for each small FSP, the duration in seconds for the sample creations, the names of non-linear DGs.
- Return type:
list, list, float, list
- data_sampler.create_all_fsp_samples(dp, dq, fsps, non_linear_dg_names)
Create all FSP samples for the Convolution based simulations.
- Parameters:
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
fsps (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe of relevant data for the fsps.
non_linear_dg_names (list[str]) – names of not linear DGs.
- Returns:
profiles for FSP, profiles for small FSP, duration for sample generation.
- Return type:
list, list, float
- data_sampler.create_all_fsp_samples_sq(dp, dq, fsps, non_linear_dg_names)
Create all FSP samples for the Convolution based simulations.
- Parameters:
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
fsps (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe of relevant data for the fsps.
non_linear_dg_names (list[str]) – names of not linear DGs.
- Returns:
profiles for FSP, profiles for small FSP, duration for sample generation.
- Return type:
list, list, float
- data_sampler.create_load_samples(no_samples, net, distribution, flex_loads, rng)
Creation of {no_samples} of new [P, Q] for each load FSP. These new [P,Q] are a flexibility activation [ΔP, ΔQ] applied on the initial output [P_0, Q_0] of each load FSP.
- Parameters:
no_samples (int) – Amount of shifts that the function will create.
net (pandapower.network) – PandaPower network in which the simulations are performed.
distribution (str) – Type of distribution by which the new [P,Q] samples are obtained.
flex_loads (list[int]) – Which Loads are considered FSPs.
rng (np.random) – Function by which the random numbers are generated.
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each load FSP, for the {no_samples}, the duration in seconds for the sample creations [float].
- Return type:
list, float
- data_sampler.create_samples(no_samples, net_sgen, distribution, keep_mp, rng, non_lin_fsps=[])
Creation of {no_samples} of new [P, Q] for each DG FSP. These new [P,Q] are a flexibility activation [ΔP, ΔQ] applied on the initial output [P_0, Q_0] of each DG FSP.
- Parameters:
no_samples (int) – Amount of shifts that the function will create, [int].
net_sgen (pandas.dataframe (pandapower)) – PandaPower network sgen.
distribution (str) – Type of distribution by which the new [P,Q] samples are obtained.
keep_mp (bool) – Boolean whether the DG FSP shifts only concern the output power factor (keeping maximum output power), or can also reduce the DG FSP power output/consumption.
rng (np.random) – Function by which the random numbers are generated.
non_lin_fsps (list[int]) – FSPs that only offer 2 setpoint options (full or no curtailment).
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each DG FSP, for the {no_samples}, the duration in seconds for the sample creations [float].
- Return type:
list, float
- data_sampler.get_fsps(comps, comp_no_list)
Get important information for FSPs.
- Parameters:
comps (pandas.dataframe (pandapower)) – network components.
comp_no_list (list[int]) – list of FSPs numbers in the network.
- Returns:
relevant FSP information.
- Return type:
pandas.dataframe
- data_sampler.get_fsps_with_idx(comps, comp_no_list)
Get important information for FSPs.
- Parameters:
comps (pandas.dataframe (pandapower)) – network components.
comp_no_list (list[int]) – list of FSPs numbers in the network.
- Returns:
relevant FSP information, names of ordered FSPs.
- Return type:
pandas.dataframe, list
- data_sampler.get_non_linear_comp(comps, non_linear_no)
Get names of not linear FSPs.
- Parameters:
comps (pandas.dataframe (pandapower)) – network components.
non_linear_no (list[int]) – number of not linear FSPs.
- Returns:
names of not linear FSPs.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.get_oltcs(comps, comp_no_list)
Get important information for FSPs.
- Parameters:
comps (pandas.dataframe (pandapower)) – network components.
comp_no_list (list[int]) – list of FSPs numbers in the network.
- Returns:
relevant FSP information.
- Return type:
pandas.dataframe
- data_sampler.profile_creation(no_samples, net, distribution, keep_mp, services='DG Only', flexible_loads=[], flexible_dg=[], non_lin_dgs=[])
Creation of {no_samples} of new [P, Q] for each FSP. These new [P,Q] are a flexibility activation [ΔP, ΔQ] applied on the initial output [P_0, Q_0] of each FSP. Based on the services (i.e. DG, Load, or Both), the more specific functions for sample creation are called.
- Parameters:
no_samples (int) – Amount of shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
net (pandapower.network) – PandaPower network in which the simulations are performed.
distribution (str) – Type of distribution by which the new [P,Q] samples are obtained.
keep_mp (bool) – Boolean whether the DG FSP shifts only concern the output power factor (keeping maximum output power), or can also reduce the DG FSP power output/consumption.
services (str) – If FSPs are DG, Loads or both.
flexible_loads (list[int]) – Which Loads are considered FSPs.
flexible_dg (list[int]) – Which DG are considered FSPs.
non_lin_dgs (list[int]) – Which FSP DGs are considered non-linear.
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each FSP, for all power flow simulations, the duration in seconds for the sample creations.
- Return type:
list, float
- data_sampler.profile_creation_bf(dp, dq, net, services='DG Only', flexible_loads=[], flexible_dgs=[], non_linear_dgs=[])
Creation of {no_samples} of new [P, Q] for each FSP for the Brute Force case. These new [P,Q] are a flexibility activation [ΔP, ΔQ] applied on the initial output [P_0, Q_0] of each FSP. Based on the services (i.e. DG, Load, or Both), the more specific functions for sample creation are called.
- Parameters:
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
net (pandapower.network) – PandaPower network in which the simulations are performed.
services (str) – If FSPs are DG, Loads or both.
flexible_loads (list[int]) – Which Loads are considered FSPs.
flexible_dgs (list[int]) – Which DG are considered FSPs.
non_linear_dgs (list[int]) – Which FSP DGs are considered non-linear.
- Returns:
The new active and reactive power for each FSP, for all power flow simulations, the active and reactive power for each small FSP, the duration in seconds for the sample creations, the names of non-linear DGs, the number of samples.
- Return type:
list, list, float, list, int
- data_sampler.sample_from_rng(distribution, no_samples_dg, dof, rng)
Based on the type of distribution, this function generates {no_samples_dg} for the flexibility activations which do not yet concern for the limits of each FSP and will later be applied on each FSP.
- Parameters:
distribution (str) – Type of distribution used for the data generation.
no_samples_dg (int) – Number of samples to be generated.
dof (int (1 or 2)) – Generated based on the ‘keep_mp’ variable. If dof=1, the random number generated for the active power P also defines the shift for the reactive power Q to keep S constant.
rng (numpy.random) – RNG function to be used to generate the data, is defined outside of the function to return the same results at each simulation (through a seed) but to avoid returning the same numbers if it is called multiple times in one simulation.
- Returns:
array of generated random values to be used for the FSP activations.
- Return type:
np.array
- data_sampler.sample_fsp_thorough_points(fsp, dp, dq)
Sample FSP shifts for all spectrum in dp, dq resolution.
- Parameters:
fsp (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe of relevant data for the fsps.
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
- Returns:
p,q values as setpoints for the FSP shifts.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.sample_fsp_thorough_points_sq(fsp, dp, dq)
Sample FSP shifts for all spectrum in dp, dq resolution.
- Parameters:
fsp (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe of relevant data for the fsps.
dp (float) – Resolution in active power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
dq (float) – Resolution in reactive power shifts that the algorithm will create and run.
- Returns:
p,q values as setpoints for the FSP shifts.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.sample_new_load_point(loads, random_p, no_samples, flex_loads=[])
This function is called to apply the generated random shifts on Load FSPs. Based on the random values generated for active and reactive power shifts, it checks that: (1) The active power shift percentages are between [0%, 100%], to avoid negative or increased consumption values (2) The reactive power shifts will not cause abs(S new) > abs(S initial).
- Parameters:
loads (pandas.dataframe) – Load FSP.
random_p (numpy array) – Loop values for the P Q shifts.
no_samples (int) – Number of samples for the applied shifts.
flex_loads (list) – Which loads of flexible out of all the network loads. If empty, it is assumed that all loads are flexible (since this function is called when at least 1 load is flexible.
- Returns:
no_samples of new P and Q values for the Load FSPs.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.sample_new_non_mp_point(sgen, random_p, no_samples, non_lin_fsps=[])
This function is called when keep_mp is false for DG FSPs. Based on the random values generated for active and reactive power shifts, it checks that: (1) The active power shift percentages are between [0%, 100%], to avoid negative or increased generation values. (2) The reactive power shifts will not cause abs(S new) > abs(S initial).
- Parameters:
sgen (pandas.dataframe) – DG FSP.
random_p (numpy array) – Loop values for the P shift.
no_samples (int) – Number of samples for the applied shifts.
non_lin_fsps (list) – Number of not linear FSPs.
- Returns:
no_samples of new P and Q values for the DG FSPs.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.sample_new_point(sgen, random_p, no_samples, non_lin_fsps=[])
This function is called when the keep_mp is true for DG FSPs. Based on the random values generated for active power shifts, it applies the shifts on P, and applies shifts is Q which will keep the S of the DG FSP same as the initial.
- Parameters:
sgen (pandas.dataframe) – DG FSP.
random_p (numpy array) – Loop values for the P shift.
no_samples (int) – Number of samples for the applied shifts.
non_lin_fsps (list) – Number of not linear FSPs.
- Returns:
{no_samples} of new P and Q values for the DG FSPs.
- Return type:
list
- data_sampler.sample_non_lin_fsp(fsp, dp, dq)
Get the shifts for the non linear FSPs (this can be modified to also offer different scenarios for non-linear FSPs).
- Parameters:
fsp (pandas.dataframe) – relevant information for not linear FSPs.
dp (float) – resolution in active power shifts.
dq (float) – resolution in reactive power shifts.
- Returns:
list of new setpoints (profiles) for not linear FSPs.
- Return type:
list
Json Reader
This Python Script reads the scenario information.
- class json_reader.SettingReader(scenario_name='unaltered_network')
Class parsing through the json scenario input files, checking their validity and saving their information.
- tester()
Test that the imported information from the file is as expected and should not cause issues later.
- Returns:
- Return type:
Plotting
This Python Script includes all functions plotting the csv results.
- plotting.box_plt1(plt1_dict, acc_type)
Plot accuracy information.
- Parameters:
plt1_dict (dict) – dictionary with accuracy info.
acc_type (str) – type of accuracy.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.box_plt3(plt1_dict, est_dict)
Generate speed plots.
- Parameters:
plt1_dict (dict) – dictionary with speed information.
est_dict (dict) – estimation dictionary.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.get_estimated_times()
Get dictionaries from results of UC2.
- Parameters:
net_name (str) – network name.
- Returns:
dictionaries with info, names of accuracy columns, names of time columns.
- Return type:
dict, list, list
- plotting.get_means12(plt_dict)
Get mean values from results.
- Parameters:
plt_dict (dict) – dictionary with results.
- Returns:
dictionary with mean values.
- Return type:
dict
- plotting.get_rel_dicts(net_name)
Get dictionaries from results of UC2.
- Parameters:
net_name (str) – network name.
- Returns:
dictionaries with info, names of accuracy columns, names of time columns.
- Return type:
dict, list, list
- plotting.get_uncertainty(df, name='', plot_type='jpg')
Plot results including uncertainty.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe with results.
name (str) – name for saving.
plot_type (str) – type of figure to be saved.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.get_uncertainty_interpret(uncert_df, safe_df, ones_df, name='', plot_type='pdf', extra=[])
Plot results including uncertainty.
- Parameters:
uncert_df (pandas.dataframe) – uncertainty dataframe.
safe_df (pandas.dataframe) – certain dataframe.
ones_df (pandas.dataframe) – reachable dataframe.
name (str) – name to save results.
plot_type (str) – type of plot to save in.
extra (list) – initial P,Q values pixel location.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_feasible_and_infeasible(x_flexible, y_flexible, x_non_flexible, y_non_flexible, operating_point, scenario_name, text, loc='')
Plot Monte Carlo simulation results including infeasible samples.
- Parameters:
x_flexible (list) – feasible P.
y_flexible (list) – feasible Y.
x_non_flexible (list) – infeasible P.
y_non_flexible (list) – infeasible Q.
operating_point (list[float, float]) – initial PCC p,q.
scenario_name (str) – name of used scenario.
text (str) – information accompanying plot.
loc (str) – location on disc.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_mc(x_flexible, y_flexible, x_non_flexible, y_non_flexible, operating_point, no_samples, scenario_name, dur_samples, dur_pf, loc='')
Plot Monte Carlo simulation results.
- Parameters:
x_flexible (list) – feasible P.
y_flexible (list) – feasible Y.
x_non_flexible (list) – infeasible P.
y_non_flexible (list) – infeasible Q.
operating_point (list[float, float]) – initial PCC p,q.
no_samples (int) – number of samples run.
scenario_name (str) – name of used scenario.
dur_samples (float) – duration for sample creations [s].
dur_pf (float) – duration for power flows [s].
loc (str) – location on disc.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_multi_convolution(filename: str, inf, q_loc, p_loc, text, loc='')
Plot convolution algorithm result.
- Parameters:
filename (str) – name of file with results.
inf (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe with infeasible samples.
q_loc (int) – height pixel of initial Q of PCC.
p_loc (int) – width pixel of initial P of PCC.
text (str) – information accompanying plot.
loc (str) – location on disc.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_only_feasible(x_flexible, y_flexible, operating_point, scenario_name, loc='')
Plot Monte Carlo simulation results only for feasible samples.
- Parameters:
x_flexible (list) – feasible P.
y_flexible (list) – feasible Y.
operating_point (list[float, float]) – initial PCC p,q.
scenario_name (str) – name of used scenario.
loc (str) – location on disc.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_opf_res(filename, init_pq, text)
Plot the OPF results.
- Parameters:
filename (str) – name of the OPF results to get for the plot.
init_pq (list[floats]) – initial active and reactive power of the PCC.
text (str) – information accompanying plot.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- plotting.plot_uc3(net1, net2)
Plot use case 3 figures.
- Parameters:
net1 (str) – network 1.
net2 (str) – network 2.
- Returns:
- Return type:
Scenario Setup
This Python Script includes all functions setting up the network and scenario parameters.
- scenario_setup.apply_cs(net, settings)
Apply CS scenario shifts on the network
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – Network model for scenario
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
network updated for the USS# case, network new PCC P,Q (y)
- Return type:
pandapower.network, list[float, float]
- scenario_setup.apply_tss(net, settings)
Apply TSS scenario shifts on the network
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – Network model for scenario
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
network updated for the USS# case, network new PCC P,Q (y)
- Return type:
pandapower.network, list[float, float]
- scenario_setup.apply_uss(net, settings)
Apply USS scenario shifts on the network
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – Network model for scenario
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
network updated for the USS# case, network new PCC P,Q (y)
- Return type:
pandapower.network, list[float, float]
- scenario_setup.get_fsp(settings)
Get indices of FSPs if any of them are specified as -1. This value , -1, is used to say ‘I do not know the indices but all components of type x are assumed FSPs
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
updated settings object
- Return type:
object
- scenario_setup.get_network(settings)
Gen the network specified in settings. Currently, only “CIGRE MV” with der “pv_wind” is implemented
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
network model
- Return type:
pandapower.network
- scenario_setup.get_observable_lines_buses(settings)
Get indices of observable lines and buses if any of them are specified as -1. This value , -1, is used to say ‘I do not know the indices but all components of type x are assumed observable
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
updated settings object
- Return type:
object
- scenario_setup.get_operating_point(settings)
Get network PCC P,Q (y)
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
Network PCC P,Q (y)
- Return type:
list[float, float]
- scenario_setup.get_unobservable_lines_buses_indices(settings)
Gen indices of network unobservable lines (all lines not specified as observable)
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
updated settings object
- Return type:
object
- scenario_setup.rand_resample(net, no_change_loads, no_change_dgs, rng, std_cap_l, std_pf_l, std_cap_dg, std_pf_dg)
Randomly sample Operating Condition shift for adaptability case study
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – Network model for scenario
no_change_loads (list) – loads not to change (FSPs)
no_change_dgs (list) – DGS not to change (FSPs)
rng (numpy.random) – object to sample random values from
std_cap_l (float) – standard deviation for load capacities
std_pf_l (float) – standard deviation for load power factor
std_cap_dg (float) – standard deviation for DG capacities
std_pf_dg (float) – standard deviation for DG power factor
- Returns:
network and used random function
- Return type:
pandapower.network, numpy.random
- scenario_setup.update_settings(settings)
Update settings by changing observable and unobservable bus and line information based on the loaded network
- Parameters:
settings (object) – json file input data
- Returns:
updated settings object
- Return type:
object
Accuracy Estimation
This Python Script includes all functions used to estimate the accuracy.
- accuracy_estimation.accuracy_brute_force(ground_truth_file, conv_results_file, decimals, operating_point)
Calculate and print mean squared error (MSE) for feasible and total points. This function calculates the mean squared error (MSE) for feasible and total points between ground truth data and results. It takes ground truth data, convex results, a number of decimals, and an operating point. It also generates a heatmap plot and saves it as an SVG file.
- Parameters:
ground_truth_file (str) – The filename of the ground truth data in CSV format.
conv_results_file (str) – The filename of the convex results data in CSV format.
decimals (int) – The number of decimals for rounding.
operating_point (list) – The operating point as [P, Q] values.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- accuracy_estimation.correct_feasible_and_infeasible(ground_truth_file, conv_results_file, inf, dur_str)
Evaluate the feasibility of points. This function evaluates the feasibility of points based on ground truth data and results. It takes ground truth data, convex results, infeasible points, and a duration string. It calculates accuracy metrics and saves them in a log file.
- Parameters:
ground_truth_file (str) – The filename of the ground truth data in CSV format.
conv_results_file (str) – The filename of the convex results data in CSV format.
inf (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame representing infeasible points.
dur_str (str) – A duration string.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- accuracy_estimation.extend_feasible_and_infeasible(ground_truth_file, conv_results_file, inf)
Extend the feasible and infeasible regions for visualization. This function extends the feasible and infeasible regions for visualization purposes. It takes a ground truth file, convex results file, and a DataFrame ‘inf’ representing infeasible points. It performs transformations on the data and generates a visualization.
- Parameters:
ground_truth_file (str) – The filename of the ground truth data in CSV format.
conv_results_file (str) – The filename of the convex results data in CSV format.
inf (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame representing infeasible points.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- accuracy_estimation.find_value_close2list(lst, voi)
Find the index and closest value in a list to a specified value. This function searches for the index and value in the input list lst that is closest to the specified value voi. It iterates through the list and calculates the absolute difference between each element and voi to find the closest match.
- Parameters:
lst (list[float]) – The list to search for the closest value.
voi (float) – The value to find the closest match for.
- Returns:
The index of the closest value in the list and the closest value itself.
- Return type:
int, float
- accuracy_estimation.get_heatmap_matrix(x_flex, y_flex, step_p, step_q, x_axis, y_axis)
Generate a heatmap matrix based on provided coordinates. This function generates a heatmap matrix where specific coordinates in the matrix are incremented based on the provided x_flex and y_flex coordinates. The matrix dimensions are determined by x_axis and y_axis, and the spacing between points is defined by step_p and step_q.
- Parameters:
x_flex (list[float]) – List of x-coordinates to increment in the heatmap matrix.
y_flex (list[float]) – List of y-coordinates to increment in the heatmap matrix.
step_p (float) – Spacing between x-axis points.
step_q (float) – Spacing between y-axis points.
x_axis (list[float]) – List of x-axis values representing the matrix’s x-coordinates.
y_axis (list[float]) – List of y-axis values representing the matrix’s y-coordinates.
- Returns:
A heatmap matrix with incremented coordinates and values normalized to the maximum value.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- accuracy_estimation.get_inf_matrix(x_flex, y_flex, step_p, step_q, x_axis, y_axis)
Generate the non-feasible space matrix based on provided data. This function generates the non-feasible space matrix where specific coordinates in the matrix are marked as “1” based on the provided x_flex and y_flex coordinates. The matrix dimensions are determined by x_axis and y_axis, and the spacing between points is defined by step_p and step_q.
- Parameters:
x_flex (list[float]) – List of x-coordinates to mark as “1” in the infill matrix.
y_flex (list[float]) – List of y-coordinates to mark as “1” in the infill matrix.
step_p (float) – Spacing between x-axis points.
step_q (float) – Spacing between y-axis points.
x_axis (list[float]/numpy array) – List of x-axis values representing the matrix’s x-coordinates.
y_axis (list[float]/numpy array) – List of y-axis values representing the matrix’s y-coordinates.
- Returns:
An infill matrix with marked coordinates as “1,” along with the x and y axis values and spacing.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray, list[float], list[float], float, float
- accuracy_estimation.get_info_matrix(x_flex, y_flex, x_nflex, y_nflex, step_p, step_q, x_axis, y_axis, maxv, minv, maxl, cost, used_fsps, selected_pts, prof_flex)
Get information for the case study “DFC Improving TSOs Flexibility Shift Selection”.
- Parameters:
x_flex (list) – flexible active power points at pcc.
y_flex (list) – flexible reacitve power points at pcc.
x_nflex (list) – not-flexible active power points at pcc.
y_nflex (list) – not-flexible reactive power points at pcc.
step_p (float) – active power resolution [mw].
step_q (float) – reactive power resolution [mvar].
x_axis (list) – x-axis values.
y_axis (list) – y-axis values.
maxv (list) – maximum voltages [p.u.].
minv (list) – minimum voltages [p.u.].
maxl (list) – maximum absolute loading [%].
cost (list) – costs for flexibility point [euro].
used_fsps (list) – minimum fsps used for each flexibility point [int].
selected_pts (dictionary) – selected points to study.
prof_flex (list) – flexible profiles.
- Returns:
matrices for number of feasible combinations (feas_mat), DFC (heat_mat), non-flexible combinations (nflex_mat), minimum maximum voltages (min_vxmat), maximum maximum voltages (max_vxmat), minimum minimum voltages (min_vnmat), maximum minimum voltages (max_vnmat), minimum loading (min_lmat), maximum loading (max_lmat), minimum costs (min_cmat), maximum costs (max_cmat), minumum used FSPs (min_umat), maximum used FSPs (max_umat), values for scenarios (v_plot).
- Return type:
lists
- accuracy_estimation.info_options(x_flexible, x_non_flexible, y_flexible, y_non_flexible, dp, dq, maxv, minv, maxl, cost, used_fsps, prof_flex)
This function plots and prints information for the case study ‘DFC Improving TSOs Flexibility Shift Selection’.
- Parameters:
x_flexible (list) – flexible pcc p
x_non_flexible (list) – non-flexible pcc p
y_flexible (list) – flexible pcc q
y_non_flexible (list) – non flexible pcc q
dp (float) – active power resolution [mw]
dq (float) – reactive power resolution [mvar]
maxv (list) – maximmum voltages [p.u.]
minv (list) – minimum voltages [p.u.]
maxl (list) – maximum absolute loading [%]
cost (list) – costs for flexiiblity point [euro]
used_fsps (list) – minimum fsps used for each flexibility point [int]
prof_flex (list) – flexible profiles
- Returns:
- Return type:
- accuracy_estimation.loop_acc(ground_truth, conv_results, inf)
Calculate and return accuracy metrics for UC2 scenarios. This function calculates accuracy metrics for the UC2 scenarios based on ground truth data, convex results, and infeasible points. It takes ground truth data, convex results, infeasible points, and a name for the plot. It calculates feasibility accuracy and available accuracy and returns their averages.
- Parameters:
ground_truth (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame containing ground truth data.
conv_results (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame containing convex results.
inf (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame representing infeasible points.
- Returns:
feasibility accuracy, available accuracy, average accuracy, a placeholder 0.
- Return type:
float, float, flaot, float
- accuracy_estimation.plot_results(ground_truth, conv_results, inf, name, x_axis, y_axis)
Generate a visualization of feasible and infeasible regions. This function generates a visualization of feasible and infeasible regions using input data. It takes ground truth data, convex results, infeasible points, a name for the plot, and axis values. The regions are plotted, and the resulting plot is saved as a PDF file.
- Parameters:
ground_truth (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame containing ground truth data.
conv_results (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame containing convex results.
inf (pandas.DataFrame) – A DataFrame representing infeasible points.
name (str) – The name of the plot and output PDF file.
x_axis (list) – The x-axis values.
y_axis (list) – The y-axis values.
- Returns:
- Return type:
- accuracy_estimation.range_acc_case_study(net, settings, pcc_operating_point)
Run some simulations for range accuracy case study.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network.
settings (object) – scenario settings.
pcc_operating_point (list[float, float]) – initial PQ values at the PCC.
- Returns:
- Return type:
Utils
This Python Script includes all generic functions.
- utils.assert_limits(net, settings)
Check that the network operates within the operation limits and assert an error if not
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network
settings (object) – scenario settings
- Returns:
- Return type:
- utils.check_limits(net, settings)
Check that the network operates within the operation limits and print it
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network
settings (object) – scenario settings
- Returns:
- Return type:
- utils.check_limits_bool(net, settings)
Check that the network operates within the operation limits and return True(feasible)/False(not feasible)
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network
settings (object) – scenario settings
- Returns:
- Return type:
- utils.check_line_current_limits(net, upper_limit=100)
Check if the power flow result on the network caused respects the loading limitations in all lines
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network model
upper_limit (int/float) – upper loading percentage limit
- Returns:
True/False if the loading of any line exceeds the upper limit
- Return type:
boolean
- utils.check_trafo_current_limits(net, upper_limit=100)
Check if the power flow result on the network caused respects the loading limitations in all transformers
- Parameters:
net (pandapower.network) – network model
upper_limit (int/float) – upper loading percentage limit
- Returns:
True/False if the loading of any line exceeds the upper limit
- Return type:
boolean
- utils.check_voltage_limits(voltages, upper_limit, lower_limit)
Check if the power flow result on the network caused respects the voltage limitations in all lines
- Parameters:
voltages (list of floats) – list of component voltages to be evaluated
upper_limit (float) – upper voltage percentage limit
lower_limit (int/float) – lower voltage percentage limit [float]
- Returns:
True/False if the voltage of any component exceeds the upper limit, or is lower than the lower limit
- Return type:
boolean
- utils.create_result_df(x_flexible, x_non_flexible, y_flexible, y_non_flexible)
Sve Monte Carlo simulation result on the folder :param x_flexible: feasible P, :type x_flexible: list of floats
- Parameters:
x_non_flexible (list of floats) – infeasible P,
y_flexible (list of floats) – feasible Q,
y_non_flexible (list of floats) – infeasible Q,
- Returns:
- Return type:
- utils.fix_missing_point(mat)
- Filter in case the sampling of FSP shifts was wrong and left a point behind, it is observed in the power flow
results if the sensitivity of a pixel is 0, but the upper, lower, left, and right values are non-zero. In that case, take their average.
- Parameters:
mat (np.array) – Array with sensitivities or binary values
- Returns:
The input array fixed for these issue
- Return type:
np.array
- utils.fix_missing_pointsv2(mat)
- Filter in case the sampling of FSP shifts was wrong and left a point behind, it is observed in the power flow
results if the sensitivity of a pixel is 0, but the upper, lower, left, and right values are non-zero. In that case, take their average.
- Parameters:
mat (np.array) – Array with sensitivities or binary values
- Returns:
The input array fixed for these issue
- Return type:
np.array
- utils.fix_net(net)
Fix the initial network structure
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network for the case studies
- Returns:
fixed network
- Return type:
pandapower network
- utils.get_input_busses_pq(net, input_buses)
Get P and Q of all bus indices in {input_buses} list
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model
input_buses (list of int) – bus indices whose P,Q values are needed
- Returns:
p= list of P of busses of interest, q= list of Q of busses of interest
- Return type:
list, list
- utils.get_input_busses_v(net, input_buses)
Get voltage magnitude v and angle θ of all bus indices in {input_buses} list
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model
input_buses (list of ints) – bus indices whose v, θ values are needed
- Returns:
p= list of v of busses of interest, q= list of θ of busses of interest
- Return type:
list, list
- utils.get_input_lines_pq(net, input_lines)
Get P and Q of all line indices in {input_lines} list
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model,
input_buses (list of int) – line indices whose P,Q values are needed,
- Returns:
p= list of P of lines of interest, q= list of Q of lines of interest
- Return type:
list, list
- utils.kumaraswamymontecarlo(a, b, c, LB, UB, num_samples, rng)
Create samples using the Kumaraswamy Monte Carlo distribution
- Parameters:
a (float) – alpha
b (float) – beta
c (float) – gamma
LB (float) – lower bound
UB (float) – upper bound
num_samples (int) – number of samples
rng (numpy.random) – object to sample data from
- Returns:
samples
- Return type:
numpy array
- utils.tensor_convolve_nd_torch(image, kernel)
Apply tensor convolution
- Parameters:
image (torch tensor) – multi-dim tensor
kernel (torch tensor) – 2D tensor
- Returns:
tensor convolution result
- Return type:
torch tensor
- utils.tensor_convolve_nd_torch_half(image, kernel)
Apply tensor convolution, but with float32 types (might run into issues exceeding the maximum number)
- Parameters:
image (torch tensor) – multi-dim tensor
kernel (torch tensor) – 2D tensor
- Returns:
tensor convolution result
- Return type:
torch tensor
- utils.update_pqs(net, flex_wt=None, flex_pv=None, profile=None, scale_w=1, scale_pv=1)
Update network DG FSP P,Q based on the input values
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model
flex_wt (list of int) – Indices of flexible wind turbines,
flex_pv (list of int) – Indices of flexible pv,
profile (list of lists of floats) – P,Q values for each FSP for one iteration on the Monte Carlo algorithm
scale_w (int/float) – If a network with different wt penetration is used, this parameter will scale the wt accordingly, (default=1, no scaling)
scale_pv (int/float) – If a network with different pv penetration is used, this parameter will scale the pv accordingly, (default=1, no scaling)
- Returns:
updated network model
- Return type:
pandapower network
- utils.update_pqs2(net, flex_dg=None, profile=None)
Update network DG FSP P,Q based on the input profile
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model,
flex_dg (list of int) – Indices of flexible distributed generation,
profile (list of list of floats) – P,Q values for each FSP for one iteration on the Monte Carlo algorithm
- Returns:
updated network model
- Return type:
pandapower network
- utils.update_pqs_wl(net, flex_wt=None, flex_pv=None, profile=None, scale_w=1.0, scale_pv=1.0, load_ind=[])
Update network FSP P,Q including loads based on the input values
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model
flex_wt (list of int) – indices of flexible wind turbines
flex_pv (list of int) – indices of flexible pv,
profile (list of (FSPs) list of (P,Q) floats) – P,Q values for each FSP for one iteration on the Monte Carlo algorithm
scale_w (int/float) – if a network with different wt penetration is used, this parameter will scale the wt accordingly, (default=1, no scaling),
scale_pv (int/float) – If a network with different pv penetration is used, this parameter will scale the pv accordingly (default=1, no scaling),
load_ind (list of int) – indices of flexible loads
- Returns:
net=updated network model
- Return type:
pandaPower network
- utils.update_pqs_wl2(net, profile, load_ind=[], dg_ind=[])
Update load and distributed generator output values.
- Parameters:
net (pandapower network) – network model
profile (list) – profile with values to update
load_ind (list) – indices of loads to update
dg_ind (list) – indices of distributed generators to update
- Returns:
updated network
- Return type:
pandapower network
- utils.update_pqs_wl2_aliander(net, profile, load_ind=[], dg_ind=[])
Update PQ values using Aliander’s PGM
- Parameters:
net (pandapower model) – network model
profile (list) – values for network components
load_ind (list) – load indices to update the values
dg_ind (lost) – distributed generation indices to update the values
- Returns:
updated network model
- Return type:
pandapower network
- utils.write_conv_result(df, name)
Write results from convolution simulations
- Parameters:
df (pandas.dataframe) – dataframe with results
name (str) – name of scenario
- Returns:
- Return type:
- utils.write_result(x_flexible, x_non_flexible, y_flexible, y_non_flexible, name)
Sve Monte Carlo simulation result on the folder
- Parameters:
x_flexible (list of floats) – feasible P
x_non_flexible (list of floats) – infeasible P
y_flexible (list of floats) – feasible Q
y_non_flexible (list of floats) – infeasible Q
name (str) – name to be used in filename,
Optimal power flow
This Python Script includes the functions used for the opf.
- opf.opf_fa_pck(net1, fsps_dg=[2, 4, 6], fsps_load=[14, 16], filename='', opf_step: float = 0.1, max_curr_per: int = 100, max_volt_pu: float = 1.05, min_volt_pu: float = 0.95)
Estimate flexibility area using OPF method.
- Parameters:
net1 (pandapower network) – network.
fsps_dg (list[int]) – distributed generators offering flexibility.
fsps_load (list[int]) – loads offering flexibility.
filename (str) – name to use in the plot.
opf_step (float) – step size for optimization. Default=0.1.
max_curr_per (int) – network maximum current constraint (optional). Default=100.
max_volt_pu (float) – network maximum voltage constraint (optional). Default=1.05.
min_volt_pu (float) – network minimum voltage constraint (optional). Default=0.95.
- Returns:
- Return type:
Main
This python script is the main file calling the rest of the scripts.
VI. Files for IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid Publication Scenarios
To run use case scenarios, you can use the json files under the scenarios folder. The scripts used are under the src/SmartGridScripts/ folder
VI.A) Accuracy in Population Estimation
The result files are in the csv_results/UC1 folder. Example figures generated for these scenarios are in the folder plots/UC1
VI.B) Speed and Range Accuracy
The CSV results are under csv_results/UC2 The figures are saved under plots/UC2
VI.C) Disjoint Flexibility Areas
The result files are in the csv_results/UC3 folder. Example figures generated for these scenarios are in the folder plots/UC3
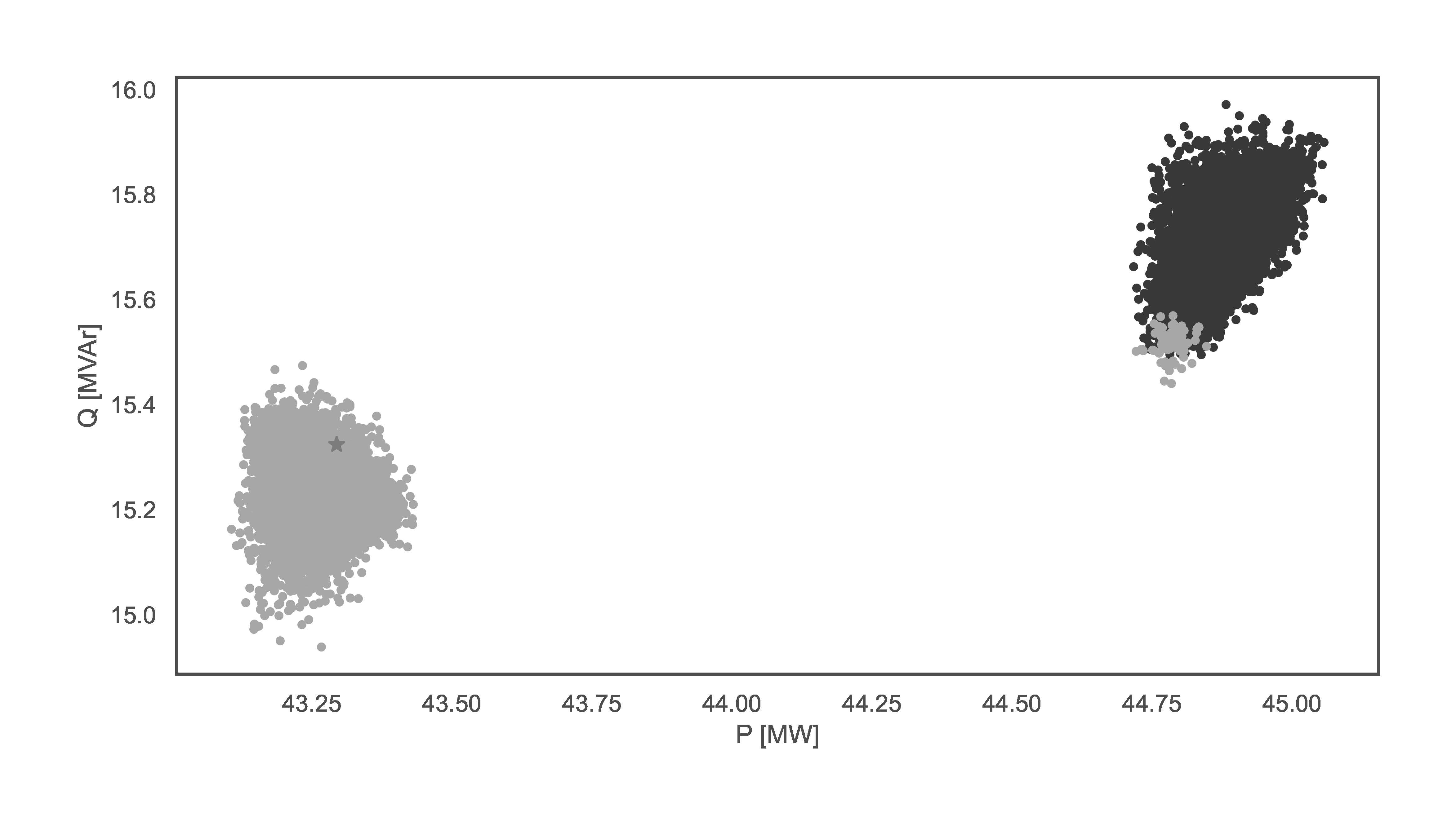
VI.D) Uncertainty Estimation for Small FSPs
The results are in the csv_results/UC4 folder. Example figure generated for the scenario is in the folder plots/UC4
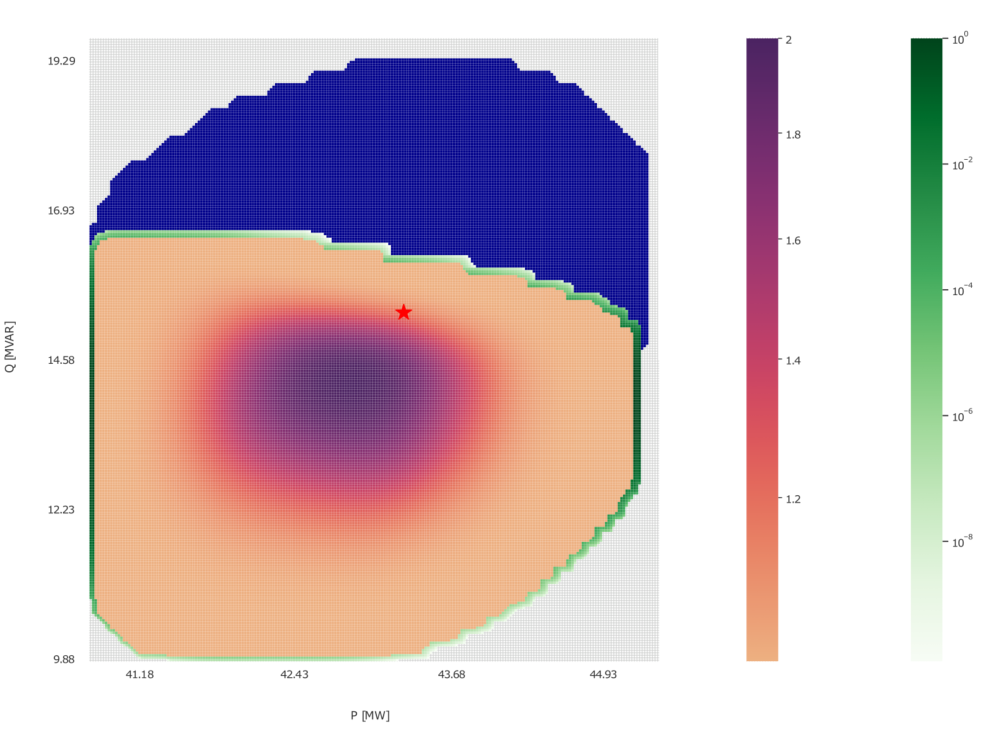
VI.E) Adaptability
Example results from the case study can be found in the csv_results/UC5 folder. Example plots are in the plots/UC5 folder:
VI.F) Case study for DFC
The results are in the csv_results/UC6 folder. Example figures generated for the scenario are in the folder plots/UC6
VI.G) Case study for OPFs
Example figure generated for this scenario is in the folder plots/UC7